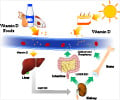
Vitamin D does more than just strengthen bones- it may influence cancer risk too! Learn how to maintain optimal levels of overall health.
- Vitamin D supports cell health, immunity, and inflammation control, reducing abnormal cell growth risks
- Low vitamin D levels may be linked to increased risks of colorectal cancer and cancer mortality
- Sun exposure, diet, and supplements can help maintain healthy vitamin D levels and overall well-being
Prevalence of serum vitamin D deficiency and insufficiency in cancer: Review of the epidemiological literature
Go to source). According to a study, between 70 and 100% of individuals in India alone are vitamin D deficient (2✔ ✔Trusted Source
Vitamin D deficiency in India: prevalence, causalities and interventions
Go to source). Nevertheless, whereas some research suggests a link, other studies fail to identify a clear cause-and-effect relationship. Let's examine vitamin D's impact on cancer risk and the scientific evidence supporting it.
Spending just 10-30 minutes in the sun can help your body produce enough vitamin D, reducing the risk of bone diseases and possibly some cancers! #vitamind #sunshinevitamin #cancerprevention #stayhealthy #medindia’
Function of Vitamin D
Vitamin D is essential to keep cells healthy. It also helps control cell proliferation, boosts immunity, and lowers inflammation.Health Benefits of Vitamin D
- Prevents aberrant cell growth and encourages normal cell activity (3✔ ✔Trusted Source
Vitamin D's role in cell proliferation and differentiation
Go to source). - Assists cells in repairing damage and avoiding cancer-causing mutations (4✔ ✔Trusted Source
Vitamin D and cancer: a review of molecular mechanisms
Go to source). - Assists the immune system in locating and eliminating dangerous cells (5✔ ✔Trusted Source
Vitamin D immunoregulation through dendritic cells
Go to source).
Link Between Vitamin D and the Risk of Cancer
The connection between vitamin D deficiency and cancer has been the subject of numerous investigations. This is what researchers discovered:- Colorectal Cancer: Higher vitamin D levels have been linked to a lower risk of colorectal cancer (6✔ ✔Trusted Source
Vitamin D and Colorectal Cancer: Current Perspectives and Future Directions
Go to source). - Lung and breast cancer: There is no significant correlation between vitamin D levels and the risk of developing lung or breast cancer (7✔ ✔Trusted Source
Vitamin D in the cancer patient
Go to source). - Pancreatic and Prostate Cancer: Extremely high vitamin D levels may potentially be associated with an increased risk of pancreatic and prostate cancer (8✔ ✔Trusted Source
Vitamin D and pancreatic cancer
Go to source).

Vitamin D Deficiency and Cancer Mortality
According to a meta-analysis of several research, those with lower vitamin D levels were more likely to pass away from the disease (9✔ ✔Trusted SourceWorsening severity of vitamin D deficiency is associated with increased length of stay, surgical intensive care unit cost, and mortality rate in surgical intensive care unit patients
Go to source). Scientists stress that vitamin D deficiency by itself does not directly cause cancer, even though these studies point to a possible link. Rather, it might make people more susceptible to the illness, particularly when paired with other risk factors like smoking, eating poorly, and not exercising.
How to Keep Your Vitamin D Levels in Check
It's critical to make sure you are getting enough vitamin D because a lack of it may increase your chance of developing cancer.- Exposure to Sunlight: Vitamin D levels can be naturally raised by spending ten to thirty minutes in the sun a few times a week.
- Diet: Vitamin D is found in foods including eggs, fatty fish, fortified dairy products, and mushrooms.
- Supplements: Supplements can be helpful if it's hard to obtain enough vitamin D from food and sunlight, but it's essential to receive advice from a doctor about the proper dosage.
A healthy lifestyle, routine checkups, and avoiding recognized cancer hazards including processed foods and smoking are just a few of the many components that go into preventing cancer. For individualized guidance, it's advisable to speak with a healthcare professional if you have concerns about your vitamin D levels.
References:
- Prevalence of serum vitamin D deficiency and insufficiency in cancer: Review of the epidemiological literature - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22977487/)
- Vitamin D deficiency in India: prevalence, causalities and interventions - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24566435/)
- Vitamin D's role in cell proliferation and differentiation - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18844838/)
- Vitamin D and cancer: a review of molecular mechanisms - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22168439/)
- Vitamin D immunoregulation through dendritic cells - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27040466/)
- Vitamin D and Colorectal Cancer: Current Perspectives and Future Directions - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36258716/)
- Vitamin D in the cancer patient - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23912386/)
- Vitamin D and pancreatic cancer - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18504144/)
- Worsening severity of vitamin D deficiency is associated with increased length of stay, surgical intensive care unit cost, and mortality rate in surgical intensive care unit patients - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22325335/)
Source-Medindia