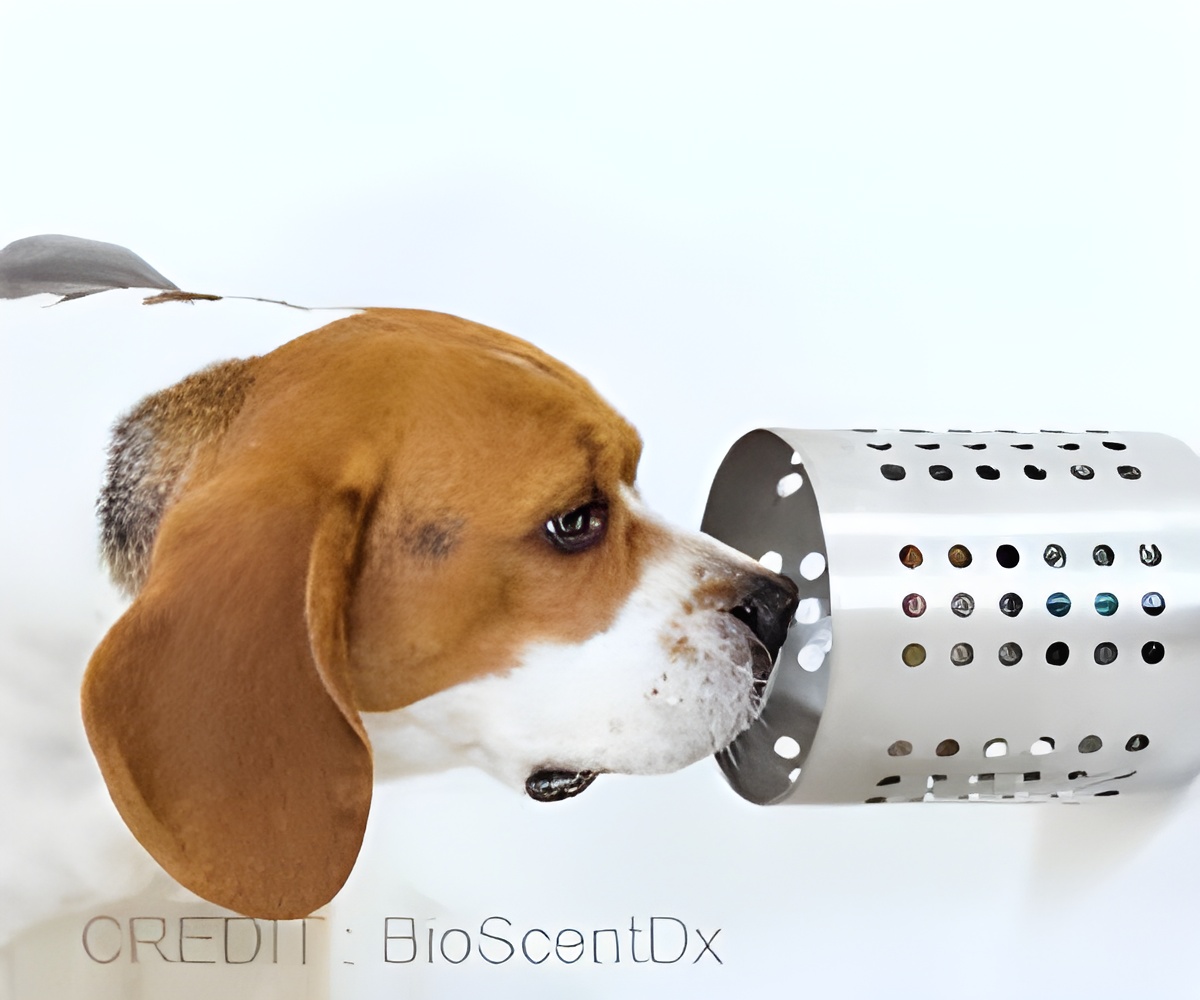
New study examined the safety, effectiveness, and practicality of utilizing trained scent dogs in clinical and public situations for COVID-19 screening.

Evaluating the Utilization of Trained Scent Dogs in COVID-19 Screening
The magic lies in their highly evolved noses, with physical and neural optimizations for smell. Dogs have hundreds of millions of olfactory receptors, compared to roughly five to six million for humans, and a full third of their brains are devoted to interpreting smells (1✔ ✔Trusted SourceScent dog identification of samples from COVID-19 patients - a pilot study
Go to source), compared to a scant 5% in human brains. All these enhancements mean that dogs can detect very low concentrations of odors associated with COVID infections.
‘Trained scent dogs can be effectively utilized to provide quick, and accurate results in COVID-19 detection, thereby reducing the spread of infection.#COVID-19 #ScentDogs #AntigenTesting’





In some scenarios the dog gave the person a quick sniff, sitting down to indicate the presence of COVID. In others, the dog was given a sweat sample to smell, a process that could take a few minutes.The speed is especially important in situations like the earlier phase of the pandemic when a gap of days between test and result could mean an exponential rise in infections if the person was positive, or scenarios that involve a high volume of people (2✔ ✔Trusted Source
Use of trained scent dogs for detection of COVID-19 and evidence of cost-saving
Go to source).
Scent dogs such as beagles, basset hounds, and coonhounds would be the ideal dog for the task, given their natural tendencies to rely on odors to relate to the world, but the studies showed a variety of other dogs are up to the challenge.
Given a few weeks of training, puppies and older dogs, males and females, purebreds, and mixed breeds all performed admirably. In one study, a problematic pit bull terrier that had been abused found a second chance by becoming a perfectly capable COVID detector.
Despite these glowing reviews, there remain challenges to placing man’s best friend in the mainstream of medical diagnosis, although animals have proven successful in the detection of other conditions, such as diabetes and cancer.
Advertisement
Sniffer dogs performance is stable over time in detecting COVID-19 positive samples and agrees with the rapid antigen test in the field
Go to source).
After conducting a comprehensive review including 29 peer-reviewed studies — that includes more than 400 scientists from over 30 countries and 31,000 samples, researchers believe that scent dogs deserve their place as a serious diagnostic methodology that could be particularly useful during future pandemics, potentially as part of rapid routine health screenings in public spaces.
Advertisement
The last thing to note is that dogs not only detect the COVID-19 virus faster, they can do so in a non-intrusive manner, without the environmental impact that comes with single-use plastics.
References:
- Scent dog identification of samples from COVID-19 patients – a pilot study - (https://bmcinfectdis.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12879-020-05281-3)
- Use of trained scent dogs for detection of COVID-19 and evidence of cost-saving - (https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmed.2022.1006315/full)
- Sniffer dogs performance is stable over time in detecting COVID-19 positive samples and agrees with the rapid antigen test in the field - (https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-023-30897-1)
Source-Eurekalert