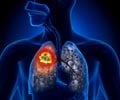
EarlyCDT®-Lung Test is a new diagnostic autoantibody test for early detection of lung cancer that allows grouping of patients according to their risk of developing lung cancer.
‘Auto antibody test followed by CT scan in risky patients cause a significant decrease in late stage diagnosis of lung cancer and all cause and lung cancer specific mortality.’
Read More..




The test identifies 41 percent of lung cancers with a high specificity of 90 percent, compared to CT scanning, which identifies 67 percent of lung cancers but with a low specificity of around 49 percent. Specificity refers to a test’s ability to correctly identify those who are negative for a disease. Read More..
Sullivan and his team sought to determine whether using the EarlyCDT®-Lung Test, followed by X-ray and CT scanning, could identify those at high risk of lung cancer and reduce the incidence of patients with late-stage lung cancer or unclassified presentation (U) at diagnosis, compared to standard clinical practice.
To answer this question, Sullivan randomized 12,208 participants aged 50 to 75 who had a high risk of developing lung cancer over the next 24 months to either the study intervention or standard practice in the United Kingdom. Test positive patients were offered a chest X-ray followed by a non-contrast thoracic CT scan. If the initial CT scan revealed no evidence of lung cancer then subsequent CT scans were offered 6 monthly for 24 months.
Individuals with abnormalities were followed up over the study period or referred for clinical care as appropriate. All individuals entering the study were followed up via trial monitoring software linked to Scottish Health Records including the Scottish Cancer Registry.
Sullivan’s team discovered that 127 lung cancers were diagnosed in the study period (56 in the intervention group and 71 in the control arm) and 9.8 percent of the intervention group had a positive EarlyCDT-Lung test and 3.4 percent (n=18) of these were diagnosed with lung cancer in the study period.
Advertisement
Sullivan added that significantly fewer participants in the intervention group were diagnosed at a late-stage compared with the control group (33 vs 52).
Advertisement
Source-Eurekalert