A new Ebola virus study has shown promising preliminary results, preventing disease in infected nonhuman primates using monoclonal antibodies, resulting from a widespread scientific collaboration.

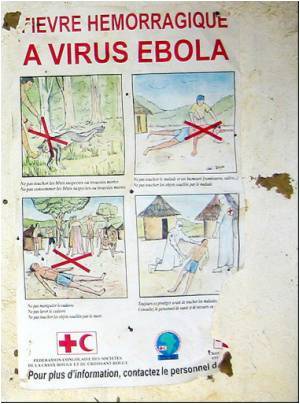
Ebola virus, which causes hemorrhagic fever with human case fatality rates as high as 90 percent, has been responsible for numerous deaths in central Africa over the past several months. In addition to being a global health concern, the virus also is considered a potential biological threat agent. Currently there are no available vaccines or treatments approved for use in humans.
The work is the culmination of more than a decade of effort between government and industry partners. According to lead investigator Gene Olinger, Ph.D., a virologist at the U.S. Army Medical Research Institute of Infectious Diseases (USAMRIID), this consortium of investigators has taken very distinct technologies and combined them to develop a cutting-edge medical countermeasure against a lethal viral disease.
"It is rare that an antiviral compound prevents Ebola virus infection with limited to no morbidity in treated animals at any point of treatment following infection by this lethal virus," said Olinger. "Until recently, attempts to utilize antibodies to provide protection against Ebola virus have been met with failure. The level of protection against disease that we saw with MB-003 was impressive."
In addition, the production method used in this study offers the potential to make an economical and effective medical countermeasure, according to the authors. Initially developed as a monoclonal antibody cocktail in the mouse model, MB-003 was successfully humanized and then produced in the tobacco plant-based production system.
"We were pleased to see how well the humanized mAbs of MB-003 performed," said Larry Zeitlin, Ph.D., president of Mapp Biopharmaceutical and senior author on the study. "We also were pleasantly surprised by the superiority of the plant-derived mAbs compared to the same mAbs produced in traditional mammalian cell culture."
Advertisement
"Our GMP facility can generate a new antibody lot in two weeks to rapidly address new threats and new outbreaks," said Bratcher.
Advertisement
Source-Eurekalert