A newly engineered T cells showed potent anti-cancer activity against tumours while minimizing reactivity against normal tissues in a mouse model of human ovarian cancer.
Identifying which antigens a patient's tumour cells express is the cornerstone of designing cancer therapy for that individual. But some of these tumour antigens are also expressed on normal cells, inching personalized therapy back to the original problem.
T cells made to express a protein called CAR, for chimeric antigen receptor, are engineered by grafting a portion of a tumour-specific antibody onto an immune cell, allowing them to recognize antigens on the cell surface.
Early first-generation CARs had one signaling domain for T-cell activation. Second-generation CARs are more commonly used and have two signaling domains within the immune cell, one for T-cell activation and another for T- cell costimulation to boost the T cell's function.
Importantly, CARs allow patients' T cells to recognize tumor antigens and kill certain tumour cells. A large number of tumor-specific, cancer-fighting CAR T cells can be generated in a specialized lab using patients' own T cells, which are then infused back into them for therapy.
Despite promising clinical results, it is now recognized that some CAR-based therapies may involve toxicity against normal tissues that express low amounts of the targeted tumor-associated antigen.
Advertisement
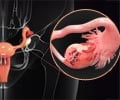
The two CARs carry different antigen specificity-mesothelin and a-folate receptor. Mesothelin is primarily associated with mesothelioma and ovarian cancer, and a-folate receptor with ovarian cancer.
Advertisement
Dual CAR T cells showed weak cytokine production against target cells expressing only one tumor-associated antigen in lab assays, similar to first-generation CAR T cells bearing the CD3 activation domain only, but demonstrated enhanced cytokine production upon encountering natural or engineered tumor cells expressing both antigens, equivalent to second-generation CAR T cells with dual, but unseparated signaling.
In a mouse model of human ovarian cancer, T cells with the dual-signaling CARs persisted at high numbers in the blood, accumulated in tumors, and showed potent anti-cancer activity against human tumors.
Dual CAR T cells were equivalent to second-generation CAR T cells in activity against tumors bearing two antigens. However, the dual-signaling CAR T cells did not react vigorously with normal tissue expressing one antigen while second- generation CAR T cells did.
"This new dual-specificity CAR approach can enhance the therapeutic efficacy of CAR T cells against cancer while minimizing reactivity against normal tissues," said Powell.
Their findings have been published in the inaugural issue of Cancer Immunology Research, the newest journal from the American Association for Cancer Research.
Source-ANI