A recent study reveals that moderate intensity regular exercise can be beneficial for breast cancer patients undergoing radiation treatment.
A recent study reveals that moderate intensity regular exercise can be beneficial for breast cancer patients undergoing radiation treatment.
This study was published in the November 15, 2006 issue of CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society. The study determined that exercise helped in improvement of oxygen capacity in patients and maintenance of red blood cells level during radiation treatment. On the other hand, obvious decrease in oxygen capacity was observed in women who did not exercise. The effect of exercise during treatment has been studied for the first time.The standard treatment of breast cancer is localized radiation therapy followed by surgical removal of the tumor. This is done to kill the remaining cancer cells in and around the primary tumor. This is a very effective combination in treating cancer.
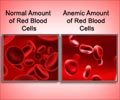
Radiation therapy may give rise to mild to moderate side effects like sunburn to an increased risk for cancer of the muscle or a sarcoma. Fatigue, anemia and depression can occur once the radiation therapy is started. These symptoms are linked with decrease in circulating red blood cells and hemoglobin that transport oxygen in the body.
According to studies, fatigue and anemia can be reduced by physical rehabilitation after the completion of the therapy. But, the effect of exercise on red blood cells has not been studied so far.
Jacqueline S. Drouin, P.T., Ph.D. of the School of Health Professions and Studies at the University of Michigan-Flint and colleagues conducted a comparative study of the effect of exercise versus no exercise during radiotherapy on red blood cell levels and on maximum oxygen capacity, a measure of physical fitness. This study was carried out in 20 women with breast cancer.
The results showed that there was no drop in levels of hemoglobin, red blood cells and hematocrit in women who went for brisk walks for 20-45 minutes 3-5 times a week during radiotherapy treatment compared to those who did not regularly exercise. In fact, a rise in levels of red blood cells and hemoglobin was seen in the active group while a drop was observed in the sedentary group. This increase is associated with increase in peak oxygen capacity.
Advertisement
Source-Medindia
GYT