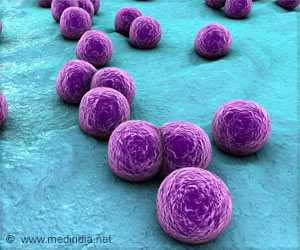
Family members of recently discharged hospital patients are at higher risk of MRSA infection. Even if the patient wasn't diagnosed with it!
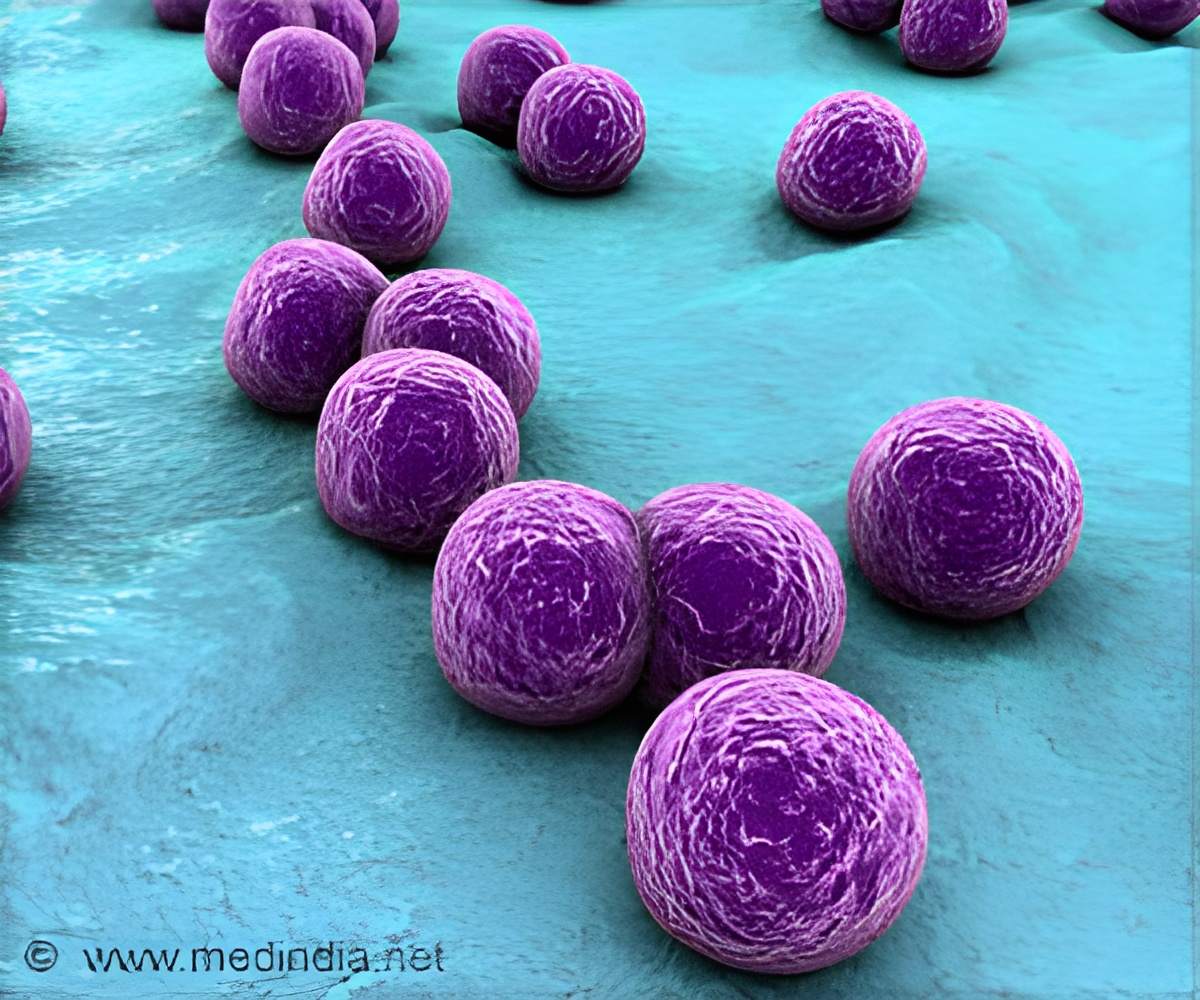
Hospitalizations among family members increase the risk of MRSA infection in a household
Go to source). This was shown by a study published in the journal Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology. It suggests hospitals play a significant role in spreading resistant bacteria into the community.
‘Hospitals are a breeding ground for Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Discharged patients, even without symptoms, can spread this dangerous superbug into the community. #MRSA #hospitalinfection #publichealth’





Longer Hospital Stays Increase MRSA Risk for Families
Researchers from the University of Iowa found that when patients were diagnosed with MRSA, the risk to their household members was even higher. The study, led by Aaron Miller, PhD, indicated that the longer a patient's hospital stay, the greater the risk to family members.“Patients can become colonised with MRSA during their hospital stay and transmit MRSA to their household members,” said Miller.
Miller recommends hospitals enhance infection control practices, including testing for MRSA colonisation at discharge. Tracking MRSA colonisation and infections among patients and their contacts could mitigate transmission effectively.
MRSA: New Insights
MRSA, known as a superbug, does not respond to common antibiotics and can be deadly if it spreads to the blood or lungs. The study reviewed 424,512 MRSA cases among 343,524 insured people, finding significant transmission risks within households.People exposed to a recently hospitalised family member with MRSA were 71 times more likely to get an infection. Even without a MRSA diagnosis, hospitalisation increased the chances of household transmission by 44 percent.
Advertisement
Reference:
- Hospitalizations among family members increase the risk of MRSA infection in a household - (https://www.cambridge.org/core/journals/infection-control-and-hospital-epidemiology/article/hospitalizations-among-family-members-increase-the-risk-of-mrsa-infection-in-a-household/F3422FED0D1A6B38B59917FE87D118D6)
Source-IANS