In profoundly deaf mice, gene therapy has partially restored hearing and balance, states study published in Nature Medicine.

Researchers led by Michelle Hastings at the Rosalind Franklin University of Medicine and Science in Chicago, Illinois, aimed at a gene called USH1C which has been implicated in the "Type 1" form of Usher syndrome.
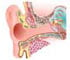
USH1C controls a protein called harmonin, which plays a vital role in hair cells -- the cells in the cochlea of the inner ear that respond to sound waves and send an electrical signal to the brain.
The team devised a tiny strand of genetic material called an antisense oligonucleotide to "switch off" a faulty version of the gene that produces truncated forms of the protein.
The therapy was injected in newborn mice that had been genetically engineered to have the mutation.
A single injection partially restored their hearing at very low frequencies, and also reduced head tossing, a behaviour caused by impaired balance.
Advertisement
After the experiment, the mice were dissected, and their cochleas were found to have grown some hair cells.
Advertisement
Last month, doctors at the Massachusetts Eye and Ear and Harvard Medical School reported on a gene drug that transformed cells in the cochlea into hair cells.
In 2012, investigators at the University of California, San Francisco targeted a fix for a faulty version of a gene called VGLUT3. The gene controls a protein that is vital for hair cells to send the signals they pick up.
Source-AFP