Health experts report a significant rise in Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) in India, linked to various responses.
Marengo Asia Hospitals, Gurugram
Go to source). The IBD Day is observed every year on May 19. The theme this year is ’IBD Has No Borders’.
‘Did You Know?
Approximately 6.8 million people worldwide live with IBD, including Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. #inflammatoryboweldisease #ibd #guthealth’





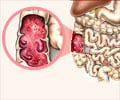
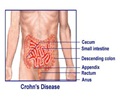
The condition is categorized mainly into Crohns disease (affecting the small intestine), ulcerative colitis (affecting the large intestine), indeterminate colitis, and microscopic colitis (diagnosed via biopsy). Approximately 6.8 million people worldwide live with IBD, including Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. #inflammatoryboweldisease #ibd #guthealth’
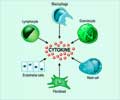
"Genetically predisposed individuals inherit susceptibility from their parents. The gut environment, particularly the balance of bacteria, plays a crucial role; a healthy gut typically contains 60-70 percent good bacteria and 30-40 percent bad bacteria," Mahesh Kumar Gupta, Senior Consultant -- Gastroenterology, Marengo Asia Hospital, Gurugram, told IANS.
Role of Genes, Gut, and Immune Responses
"Disruption in this balance, often due to poor dietary habits, lack of sleep, or excessive consumption of junk food and preservatives, can trigger inflammation. The immune system’s interaction with genetic and bacterial factors further contributes to intestinal ulcerations seen in IBD," he said.Common symptoms of IBD include bloody diarrhea, weight loss, fever, fatigue, abdominal pain, anemia, joint pain, and skin problems, among others.
A 2023 study published in the journal Lancet showed that the rising urbanization which comes with increased intake of ultra-processed foods is leading to a surge in IBD among young adults and even adolescents in India.
Advertisement
Anukalp Prakash, Lead Consultant -- Gastroenterology, CK Birla Hospital, Gurugram, told IANS that there is also an increase in pediatric cases of IBD. While the exact cause is not known, genetics may be at play, she said.
The Lancet study also blamed C-section deliveries that devoid the child of the essential gut microflora.
Further, lack of breastfeeding and excessive use of antibiotics also increase the risk of IBD. The health experts called for maintaining a healthy diet rich in fiber, staying hydrated, and avoiding preservatives.
Reference:
- Marengo Asia Hospitals, Gurugram - (https://www.marengoasiahospitals.com/hospital/marengo-asia-hospitals-gurugram)
Source-IANS