DNA methylation is related to liver disease known as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) among obese patients, research at The Translational Genomics Research Institute finds. The team also identified four genes that can cause the disease.
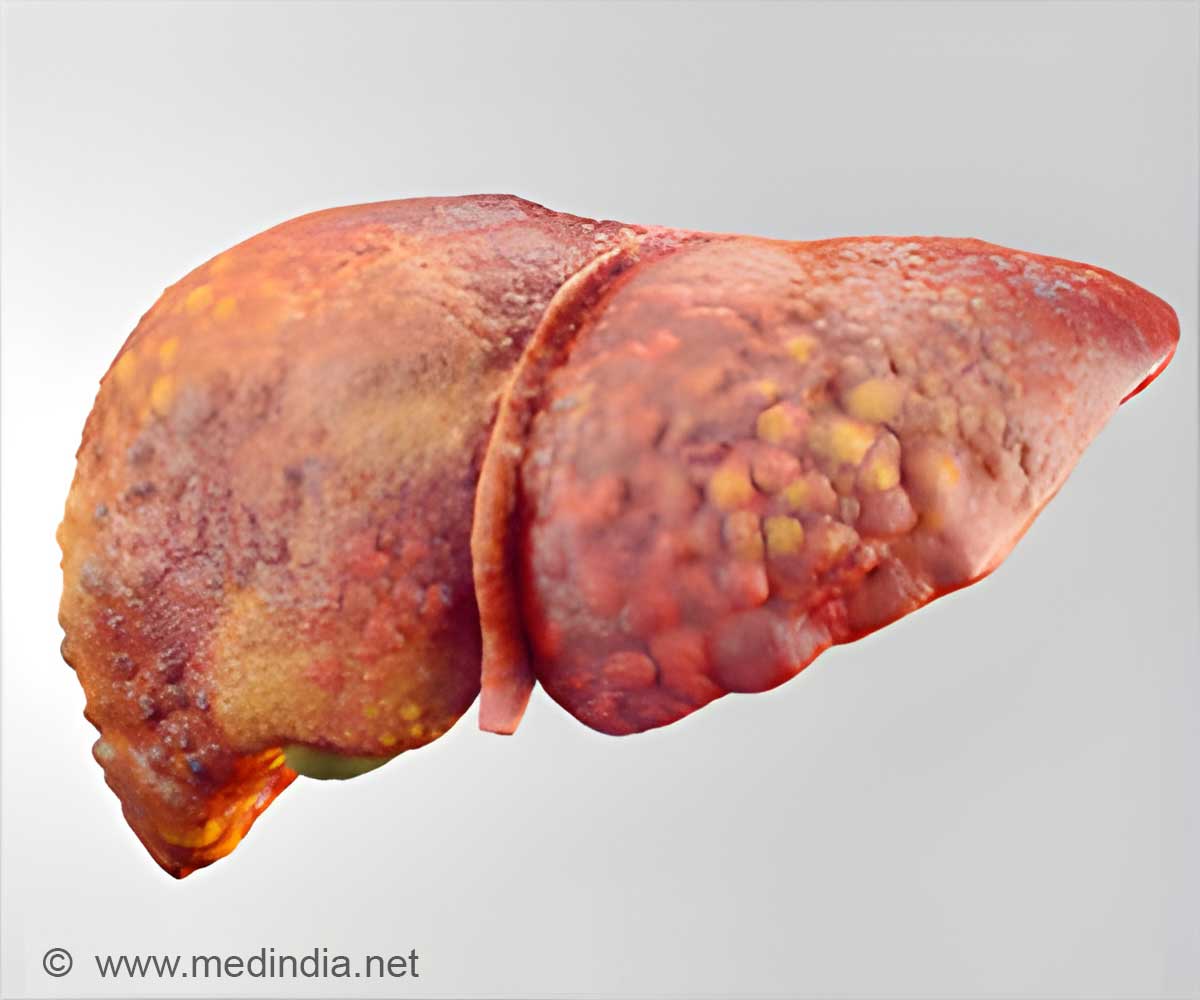
‘DNA methylation in four genes has been identified as the cause of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) among obese patients.’





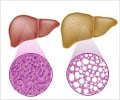
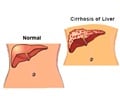
In one of the most exacting studies of its kind, TGen scientists found evidence that DNA methylation has a role in the initiation of NAFLD-related fibrosis. Obesity and insulin resistance are associated with fat accumulation in the liver, and obesity is a significant risk factor for NAFLD. Using a City of Hope computer algorithm specifically designed for the task, researchers analyzed the biopsied liver tissues of 14 obese patients with advanced fibrosis or cirrhosis of the liver, and 15 obese patients with normal livers.
"Our findings showed statistically significant evidence for differential DNA methylation between fibrotic and normal tissue samples from obese individuals," said Dr. Johanna DiStefano, a TGen Professor and head of the institute's Diabetes and Fibrotic Disease Unit.
Importantly, the study zeroed in on four genes, AQP1, FGFR2, RBP5 and MGMT, that not only were methylated in this study, but also in three previous studies that were similar, but not specifically focused on advanced fibrosis in obese NAFLD patients.
"These genes could represent targets for new therapeutics," said Dr. DiStefano, the study's senior author, who plans to pursue a larger study that would validate the initial findings in this pilot inquiry. "These approaches are yielding new insights into the pathological mechanisms underlying the development of fibrosis and cirrhosis in NAFLD."
Advertisement
Source-Eurekalert