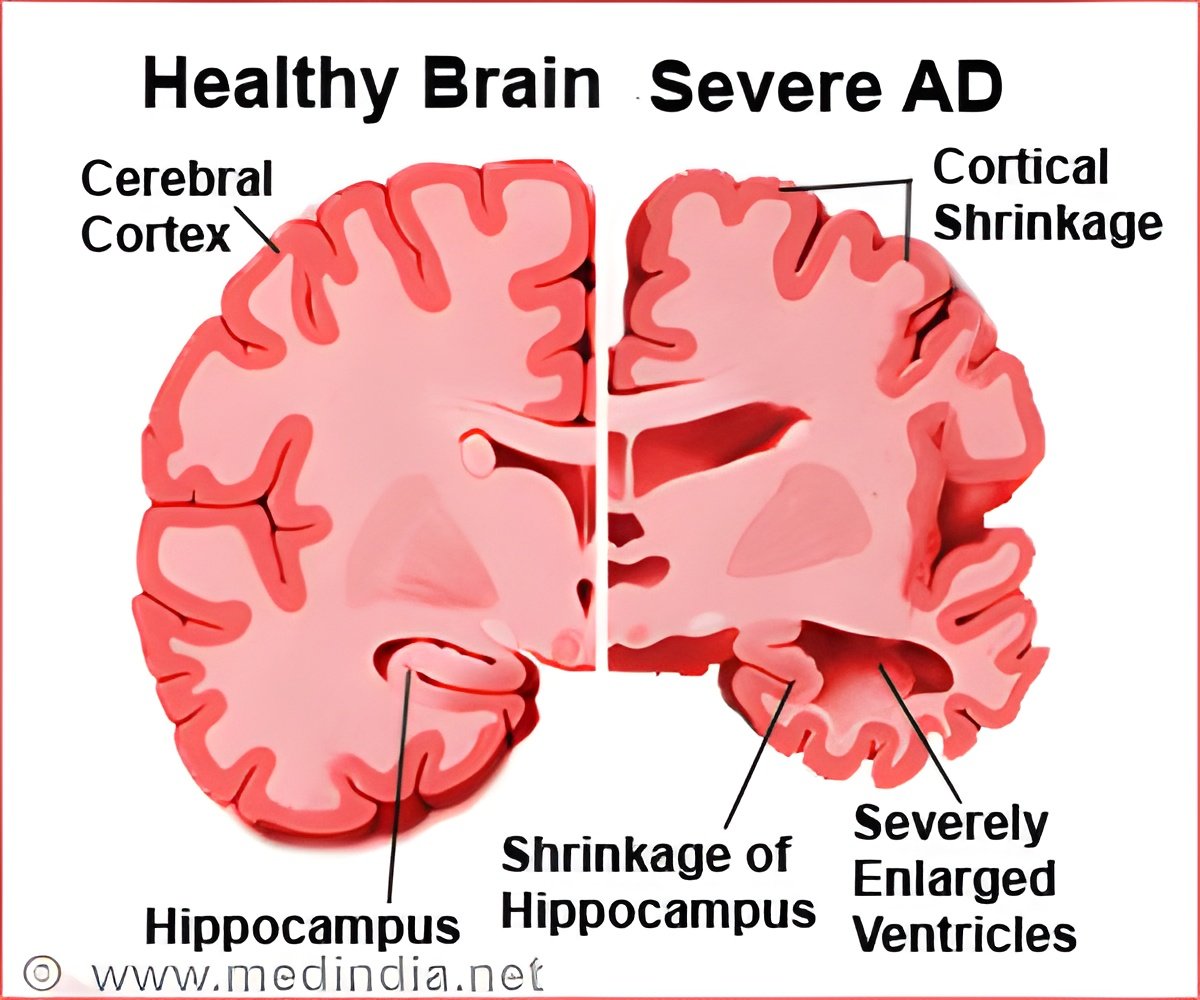
The main pathological changes of Alzheimer's disease (AD) include neurite outgrowth impairment and amyloid-beta protein-induced hippocampal neuronal injury.
In view of the fact that ginsenoside Rb1 exhibits anti-aging and anti-dementia effects, Prof. Qionglan Yuan and her team, Department of Anatomy & Neurobiology, Tongji University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China performed a study, in which ginsenoside Rb1 was used, and found that ginsenoside Rb1 promoted hippocampal neuronal neurite outgrowth and protected against neurotoxicity induced by amlyloid-beta (23-25) via a mechanism involving Akt and extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 signaling.
Related results were published in Neural Regeneration Research (Vol. 9, No. 9, 2014).
Source-Eurekalert









