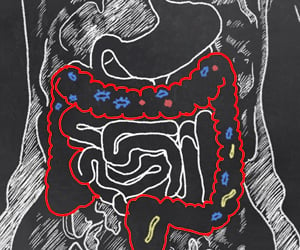
Gut microbiota is a community of microorganisms in the gut that can affect emotional and social behaviors, such as anxiety and depression in humans.
‘An essential role is played by the brain-gut-microbiota interactions in healthy humans in their emotional and social behavior.’





Brain-gut-microbiota interactions may play an important role in human health and behavior. Previous research suggests that microbiota, a community of microorganisms in the gut, can influence behavior and emotion. Rodent models have demonstrated the effects of gut microbiota on emotional and social behaviors, such as anxiety and depression. There is, however, little evidence of this in humans.
For this study the researchers sought to identify brain and behavioral characteristics of healthy women clustered by gut microbiota profiles.
METHOD
Forty women supplied fecal samples for profiling, and magnetic resonance images were taken of their brains as they viewed images of individuals, activities or things that evoked emotional responses.
Advertisement
The Bacteroides group showed greater thickness of the gray matter in the frontal cortex and insula, brain regions involved with complex processing of information. They also had larger volumes of the hippocampus, a region involved in memory processing.
Advertisement
This group's hippocampus was less active while the women were viewing negative images. They also rated higher levels of negative feelings such as anxiety, distress and irritability after looking at photos with negative images than did the Bacteroides group.
IMPACT
These results support the concept of brain-gut-microbiota interactions in healthy humans.
Researchers do not yet know whether bacteria in the gut influence the development of the brain and its activity when unpleasant emotional content is encountered, or if existing differences in the brain influence the type of bacteria that reside in the gut.
Both possibilities, however, could lead to important changes in how one thinks about human emotions.
Source-Eurekalert