Diagnostic lipid markers for metabolic syndrome and SCFAs correlate with interleukin immunoexpression in benign hyperplasia prostate tissue.
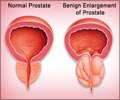
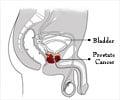
Tissue immunoexpression of IL-6 and IL-18 in aging men with BPH and MetS and their relationship with lipid parameters and gut microbiota-derived short chain fatty acids
Go to source).
Interplay of Lipid Parameters, Metabolic Syndrome, and Interleukins in Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
In this new study, researchers Weronika Ratajczak, Maria Laszczyńska, Aleksandra Rył, Barbara Dołęgowska, Olimpia Sipak, Ewa Stachowska, Marcin Słojewski, and Anna Lubkowska from Poland’s Pomeranian Medical University and State University of Applied Sciences aimed to assess whether the diagnostic lipid parameters for metabolic syndrome and short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) are related to the immunoexpression of interleukins in prostate tissue with benign hyperplasia. The study involved 103 men with BPH, who were divided into two groups depending on the presence of MetS. “We analysed tissue immunoexpression of two proinflammatory interleukins: IL-6, which is known to be involved in the development of BPH, and IL-18, which has not been analysed so far.”‘Lipid abnormalities observed in men with BPH escalate inflammation within the prostate gland. #menshealth #internationalmensday #prostatehealth’





The results of their study indicated that men with BPH + MetS in the stroma of the prostate have a significantly higher overall percentage of IL-6+ cells compared to men without MetS (p = 0.034). The analysis of IL-18 immunoexpression in prostate tissue indicated that in men with BPH + MetS, the glandular part of the prostate had a significantly higher percentage of cells with strong IL-18 expression (p = 0.040). They also noticed a relationship between tissue expression of IL-6 and IL-18 and lipid parameters (TG and HDL).
“Moreover, it has also been demonstrated for the first time that, indirectly, through SCFAs, the gut microbiota can act to prevent or create an inflammatory microenvironment in the prostate gland.”
Reference:
- Tissue immunoexpression of IL-6 and IL-18 in aging men with BPH and MetS and their relationship with lipid parameters and gut microbiota-derived short chain fatty acids - (https://aging-us.com/article/205091/text)
Source-Eurekalert