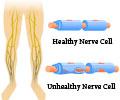
Selective inhibition of HDAC6 improved both the motor and sensory deficits in the neurological disorder, Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease.
‘HDAC6 inhibitors protect cells against neurotoxicity and have additional benefits as an anti-cancer drug.’





These building blocks can be modified chemically, for example by acetylation, to allow for further fine-tuning of the cytoskeletal stability. This is important, especially in the long axons of human motor neurons and sensory neurons. Researchers in the lab of prof. Ludo Van Den Bosch (VIB-KU Leuven) previously identified HDAC6 as an interesting target in a genetic mouse model for one of the forms of the neurological disorder Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease (CMT).
But Van Den Bosch is optimistic that HDAC6 inhibitors could play a much broader role: "Our new findings point to possible therapeutic applications for other forms of CMT, as well as for the neuronal side effects caused by chemotherapy."
"Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease can be caused by more than 80 different mutations, which has made it very difficult to pinpoint a central disease mechanism," explains Dr. Veronick Benoy from the team of Van Den Bosch. She found that selective inhibition of HDAC6 improved both the motor and sensory deficits in another genetic mouse model of CMT. "These results suggest that disturbed acetylation of 伪-tubulin may be a common hallmark of different forms of CMT.
Moreover, we found a cellular link between HDAC6 and the disease-associated protein, indicating that HDAC6 could be linked to CMT disease pathogenesis and that selective inhibition of HDAC6 with a drug could be a beneficial treatment strategy for a wide variety of CMT patients."
Advertisement
"As a side effect of chemotherapy, many patients develop peripheral neuropathies which can be extremely painful. The fact that cancer is more and more becoming a chronic disease is good news of course, but it also means that we urgently need better options to deal with side effects of the treatments."
Advertisement
Thus, HDAC6 inhibition both protected against neurotoxicity and had additional benefits as an anti-cancer drug. Van Helleputte: "The development of a painful peripheral neuropathy is the dose-limiting side effect of a variety of anti-cancer therapies. HDAC6 inhibitors could drastically improve treatment options."
Van Den Bosch believes studying the molecular mechanisms of disease processes is crucial: "It pays to go beyond compound screening of therapeutic modulators and investigate how exactly a given molecule exerts its effect. Our current results are the perfect example of a situation in which we were able to discover new potential therapeutic targets based on common mechanisms in seemingly different diseases and contexts."
Source-Eurekalert