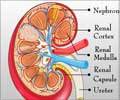
Kidney complications arise at a higher rate in patients admitted with acute critical illness without pre-existing kidney disease, says study.
- Patients with acute critical illness without underlying kidney disease, generally considered a low-risk group for kidney disease, ended up with a high risk of clinically relevant long-term kidney problems
- Examples of Acute critical illnesses included severe trauma, sepsis, myocardial infarction (MI) or post cardiac arrest syndrome (PCAS)
- Monitoring kidney function regularly of patients with acute critical illness episode without preexisting renal disease is necessary. Follow up monitoring should happen between one month to three months and then yearly afterward
Most of the studies conducted earlier have looked at patients with pre-existing kidney disease.
The study entitled ‘Renal Complications and Subsequent mortality in acute critically ill patients without pre-existing renal disease’ is a significant new finding and all clinicians and patients should be aware of this risk both in short and long term.
This study looked at 33,613 Taiwanese adult patients with no pre-existing renal disease and admitted for acute critical illness between 2000 and 2011, from the Taiwan National Health Insurance Research Database.
Each patient was matched 1:2 with controls without acute critical illness – the total number of control patients was 63,148.
The team looked at data from both the groups for outcomes that included acute kidney injury, chronic kidney disease, and end-stage renal disease.
- Patients with an acute kidney illness were at an increased risk of renal complications, with the highest incidence of developing chronic kidney disease. The incidence rates per 10 000 person-years were 78.3 for chronic kidney disease, 21.0 for end-stage renal disease, and 9.45 for acute kidney injury
- The strongest risk factors for the above three renal complications were septicemia and septic shock
- Patients with acute critical illness who subsequently developed chronic kidney disease and end-stage renal disease were at a higher risk of death
- Shih-Ting Huang MD, Tai-Yuan Ke MD, Ya-Wen Chuang MD, Cheng-Li Lin MSc, Chia-Hung Kao MD., "Renal complications and subsequent mortality in acute critically ill patients without pre-existing renal disease" CMAJ (2018) September 10;190:E1070-80. doi: 10.1503/cmaj.171382
- Acute kidney failure - (https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/kidney-failure/symptoms-causes/syc-20369048)
Source-Medindia