Severe chronic migraine can be debilitating, but botox offers a safe treatment option which can improve the quality of life of a patient.
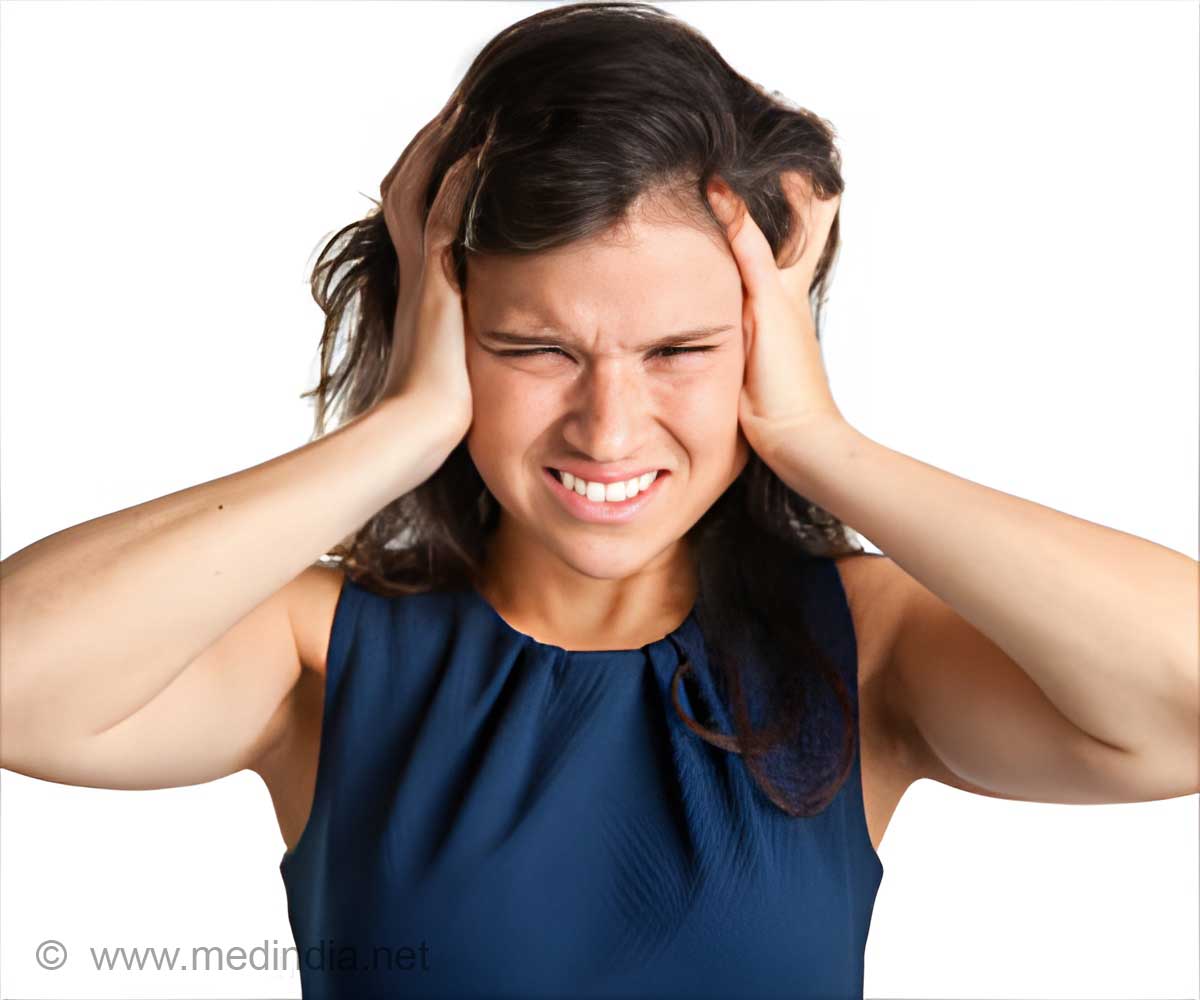

- Botox is now found to offer treatment for migraine
- Migraine is a common neurological disorder
- Botox is a neurotoxin isolated from the organism Clostridium botulinum.
Facts About Migraine
- There are more number of migraine sufferers in the U.S than the number of people with diabetes or asthma.
- In India, though there is no official count, there are considerable number of people who suffer from migraine, with more women and people affected in rural areas
- The headaches and nausea are very severe and affect the quality of life of people with migraines.
- Chronic migraine results in headaches every day which can affect the individual’s ability to cope with career and academic prospects.
- Migraine leads to depression, anxiety and sleeplessness among patients.
Chronic migraine patients were treated with Onabotulinum toxin A between February 2014 and November 2015 at the Parma Headache Centre. 52 patients were included in the study and were injected with Botox every 3 months. The patients were tested for:
- Reduction in intensity of migraines
- Disability
- Tolerance to treatment
- Depression
- Dependence on symptomatic drugs
Another study focused on the long-term benefits of using botox and whether there were any side effects caused due to the treatment measure. This study conducted by Kollewe K and colleagues is titled “Long-term treatment of chronic migraine with OnabotulinumtoxinA: efficacy, quality of life and tolerability in a real-life setting.” and published in the Journal of Neural Transmission (April 2016).
In this study, 25 females and 2 males with chronic migraine were included in the study and were treated with botox injections for an average period of 79 weeks. It was found that patients who received this treatment showed:
- Reduced incidences of migraine
- Lowered need for migraine medications
- A healthier life
- A drop in depression
Mode of Action of Botox
Though it is not fully understood, scientists believe that botox inhibits pain by blocking pain pathways in the trigeminovascular system which plays a crucial role in the headaches induced during a migraine attack.Botox for Other Body Pains
Botox has been found to provide relief for neuropathic pain, lower back pain, bladder pain and myofascial pain.Side Effects of Botox
Very few people develop side effects and none of the side effects are alarming.- Neck pain
- Drooping eyelids
- Muscular weakness
References:
- http://www.migraineresearchfoundation.org/fact-sheet.html
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4180629/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK344293/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27032774
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27048312
- https://www.migrainetrust.org/living-with-migraine/treatments/Botox