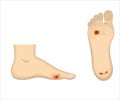
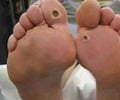
Charcot foot, a complication of diabetes that can ultimately lead to deformation and even amputation. To prevent amputation, early diagnosis and prompt treatment is needed.
- Diabetic foot is the most common and one of the preventable causes of amputation in adults
- Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial in preventing Charcot Foot progression and reducing the risk of complications
- Misdiagnosis is common, and healthcare providers should be aware of the signs and symptoms of Charcot Foot and consider it in patients with diabetes and foot-related problems
The Charcot foot in diabetes
Go to source).
Charcot foot is believed to result from a combination of peripheral neuropathy, trauma, and repetitive micro trauma. Neuropathy, a common complication of diabetes, leads to loss of sensation and proprioception (limb positioning) in the feet, making it difficult for patients to feel pain and notice changes in their feet. This can result in trauma, such as a simple sprain or twist, going unnoticed and untreated, leading to further damage.
Additionally, repetitive micro trauma, such as walking on uneven surfaces, can also contribute to the development of Charcot Foot. This repetitive stress can cause damage to the bones and joints of the foot, which may trigger an inflammatory response leading to further destruction of the tissues.
Charcot Foot is commonly found in patients with diabetes, but it can also affect those with other conditions such as arthritis or nerve damage. It is a result of a neuropathic process that affects the bones and joints of the foot, leading to the loss of sensation and the development of deformities. As a result, patients with Charcot foot often do not experience pain or discomfort, which can lead to delayed diagnosis and treatment.
Read More..
Diagnosis of Charcot Foot
Dr. Simon emphasizes the importance of early diagnosis and treatment to prevent further damage and amputation. He explains that Charcot Foot can cause significant disability, as it can lead to fractures, dislocations, and instability in the foot and ankle. Without proper treatment, the condition can progress to a point where amputation is the only option.However, diagnosing Charcot Foot can be challenging, as it can mimic other conditions such as gout, cellulitis, or osteomyelitis. The symptoms of Charcot Foot include redness, swelling, warmth, and deformity of the foot or ankle. These symptoms can be mistaken for an infection or injury, leading to misdiagnosis and delayed treatment.
Dr. Simon calls for increased awareness and education among healthcare professionals to improve the diagnosis and management of Charcot Foot. He emphasizes the need for a multidisciplinary approach, involving podiatrists, orthopedic surgeons, endocrinologists, and wound care specialists, to provide comprehensive care for patients with Charcot Foot.
Treatment for Charcot Foot typically involves immobilization of the foot and ankle, either with a cast or a brace, to prevent further damage and allow the bones and joints to heal. In some cases, surgery may be required to correct deformities or stabilize the foot and ankle. Wound care is also essential, as patients with Charcot Foot are at high risk of developing ulcers and infections.
Newer Treatments and Surgery Options for Charcot Foot
Total Contact Casting (TCC):
TCC is a type of cast that is designed to distribute weight evenly across the foot and protect the foot from further damage. It has been shown to be effective in reducing pressure and preventing complications in patients with Charcot Foot (1✔ ✔Trusted SourceMulti-Target Cinnamic Acids for Oxidative Stress and Inflammation: Design, Synthesis, Biological Evaluation and Modeling Studies
Go to source).
Custom Orthotics:
Custom orthotics are shoe inserts that are designed to support and protect the foot. They can be used to offload pressure and prevent further damage in patients with Charcot Foot (2✔ ✔Trusted SourceThe Sensitivity of Single-Trial Mu-Suppression Detection for Motor Imagery Performance as Compared to Motor Execution and Motor Observation Performance
Go to source).
Bisphosphonates:
Bisphosphonates are a type of medication that can be used to slow bone loss and promote healing in patients with Charcot Foot.External Fixation:
External fixation is a surgical procedure that involves using pins, wires, and screws to stabilize the foot and promote healing. It has been shown to be effective in treating severe cases of Charcot Foot.Arthrodesis:
Arthrodesis is a surgical procedure that involves fusing the bones of the foot together to stabilize the foot and prevent further damage. It is often used in patients with severe Charcot Foot.In conclusion, Charcot Foot is a serious condition that often goes misdiagnosed due to its similarity to other conditions. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential to prevent further damage and amputation. Healthcare professionals need to be aware of the symptoms of Charcot Foot and the importance of a multidisciplinary approach to provide comprehensive care for patients with this condition. With increased awareness and education, we can improve the diagnosis and management of Charcot Foot and improve the lives of those affected by this condition.
References :
- Multi-Target Cinnamic Acids for Oxidative Stress and Inflammation: Design, Synthesis, Biological Evaluation and Modeling Studies - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6337588/)
- The Sensitivity of Single-Trial Mu-Suppression Detection for Motor Imagery Performance as Compared to Motor Execution and Motor Observation Performance - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6728805/)
- The Charcot foot in diabetes - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21868781/)
Source-Medindia