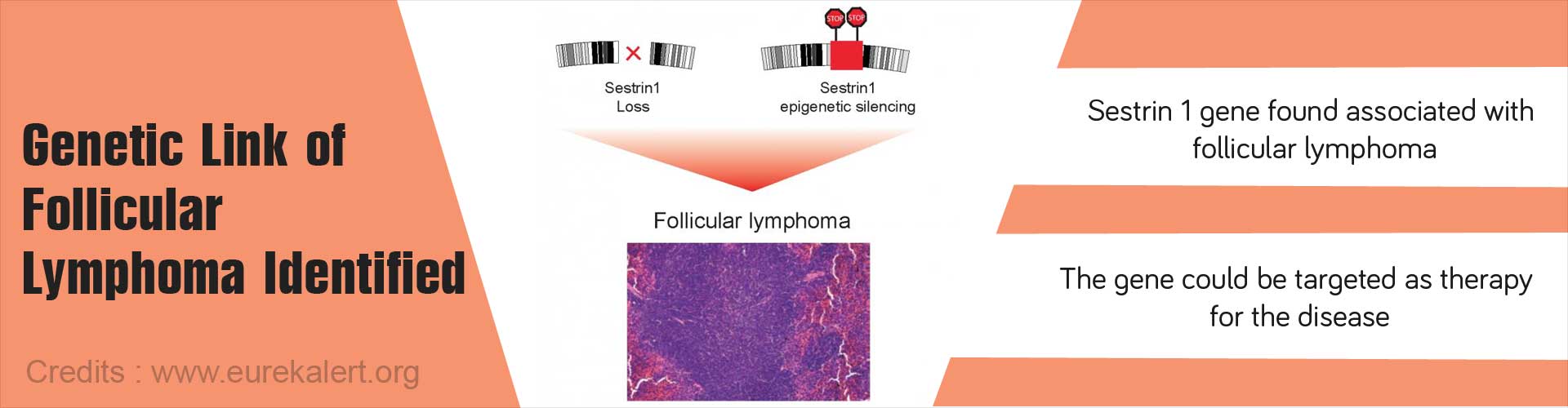
Sestrin1 gene loss of function or down regulation leads to an increased risk of follicular lymphoma.
Highlights:
- Follicular lymphoma is a type of cancer that develops slowly and is incurable
- Sestrin1 gene has now been found to be associated with the development of this type of cancer
- The gene could be targeted in the future as therapy for follicular lymphoma
Analyzing the Genome of Follicular Cancer Patients
The research team from EPFL along with collaborative scientists from the U.S and Canada analyzed the genetic test results of over 200 patients with follicular cancer.The study found that
- The gene Sestrin1 was silenced by the loss of certain genes in chromosome 6
Alterations that Affect the Expression of the Sestrin Gene
- Chromosomal translocation of chromosomes 14 and 18
- Loss of a region on chromosome 6
- Mutations in epigenetic regulators like EZH2 that block the expression of sestrin1
The current study that identified the importance of Sestrin1 gene in the development of follicular cancer is important as it can now be used to detect the risk of developing the cancer early on. It can also be used to identify patients who require therapy to control the cancer. Another important aspect is that Sestrin1 is a gene that is associated with controlling the growth of cancer; therefore, it could be associated with other cancers too.
Follicular Lymphoma
Follicular lymphoma is a type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma and is first evident as a swelling in the armpit, neck or groin. Other symptoms associated with the initial stages of this cancer are fever, night sweats and weight loss.This is one of the slow growing cancers and it constitutes about 12% of all non-Hodgkin lymphomas The incidence of non-Hodgkin lymphoma in India is
- Men - 2.9/100,000
- Women - 1.5/100,000
Significance of Sestrin1 Gene
This is the first study that highlighted the significance of Sestrin1 gene in follicular lymphoma. This gene, however, also plays an important role in other disease conditions, namely cardiac hypertrophy. The study conducted by Ruicong Xhu and colleagues from the University of Guangzhou is titled “Sestrin1 ameliorates cardiac hypertrophy via autophagy activation” and published in the Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine. Cardiac hypertrophy increases the risk for cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. Autophagy plays an important role in the mechanism that leads to cardiac hypertrophy. Sestrin1 is found to regulate autophagy. The study found that there was reduction in Sestrin1 mRNA and protein expression during cardiac hypertrophy.From the study it was evident that
- Knockdown of the Sestrin1 gene leads to an increase in cardiac hypertrophy
- Over expression of the Sestrin1 using adenovirus stopped the hypertrophy
References:
- Genetic and epigenetic inactivation of SESTRIN1 controls mTORC1 and response to EZH2 inhibition in follicular lymphoma - (http://stm.sciencemag.org/content/9/396/eaak9969)
- Follicular Lymphoma - (http://www.lymphoma.org/site/pp.asp?c=bkLTKaOQLmK8E&b=6300155)
- What is Follicular Lymphoma? - (http://www.macmillan.org.uk/information-and-support/lymphoma/lymphoma-non-hodgkin/understanding-cancer/types-of-non-hodgkin-lymphoma/follicular-lymphoma.html)