The presence of HPV antibodies in head and neck cancer patients is a good prognostic marker that can be used to determine survival rate.
Highlights
- This is one of the first studies to show that HPV antibodies are a good prognostic marker for increased patient survival with head and neck cancer.
- The presence of the HPV antibody in the blood can be used as a signal of prognosis and it is not dependent on the quantity of antibody present.
- Identification of both E6 and E7 antibodies is a better prognostic marker
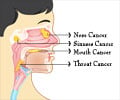
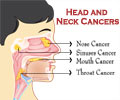
Head and Neck Cancer
Head and neck cancers include cancers that begin in the squamous cells that line the mucosal membrane. The different types of head and neck cancers include cancer of the oral cavity, salivary glands, larynx, pharynx and the paranasal sinuses and the nasal cavity.Head and neck cancer is caused mostly due to tobacco smoking and alcohol consumption, while a small percentage of head and neck cancers may also be caused due to Human Papilloma Virus (HPV) infection.
Identifying the Prognosis Marker
Blood samples of 1000 people with head and neck cancer who were diagnosed between the years 1999 and 2011 were studied.- Patients who tested positive for oncogene HPV proteins E6 or E7 had a better prognosis
- They were less likely to die when assessed after a 5 year period.
- 25% less likely to die when they showed an immune response compared to people with no immune response
Cancer Prognosis Testing
It is very important to carry out a prognosis test for cancer to determine the survival risk and to identify the best method of treatment. Every individual responds differently to cancer and a prognosis test will provide a better understanding of the response.It can be used to decide upon the course of treatment, as in some forms of cancer, rigorous chemotherapy may not be required. Some of the prognosis tests are also used to determine recurrence risk of the specific cancer.
HPV virus was earlier associated only with cancers in the oropharynx, however, now it is associated with all cancers in the head and neck region. In the current study, it was found that the HPV immune response identified among cancers that were located in the oropharynx and the larynx showed a better but similar survival risk. The risk of survival was lower among cancers in the oral cavity.
- The detection of the antibodies in the patients with head and neck cancer was an indicator of better prognosis, it was not dependent on the quantity of antibodies present.
- Testing for both E6 and E7 antibodies was a better detector of prognosis than detecting only one type of antibody.
- There was a lowered risk of dying for people who showed the presence of antibody, even among those who consumed alcohol and tobacco.
- The least survival rate was witness among smokers without any antibody for HPV.
There are two major factors which could influence prognosis of head and neck cancer patients due to infection by the HPV virus:
- Tumor Suppressor Genes: The HPV virus delineates the tumor suppressor genes among head and neck cancer patients, these genes are known to drive tumor growth.
- Immune Response: The presence of additional antibodies due to the HPV virus may have an effect on the growth and maturation of the cancer cells, leading to better prognosis. Cancers are known to evade the immune response of the host, failing to mount a suitable response, which encourages their proliferation. However, in patients with HPV infection, the immune response against the virus might lead to the destruction of cancer cells. The importance of eliciting an immune response to cancer is utilized in immunotherapy, where the immune cells of the host are used to control the growth of cancer.
Prognostic Markers in Cancer
There are some well-established factors that are considered to be good prognostic markers for cancer.- The age of the patient is an important factor in cancer prognosis. When the age is over 60 years, the prognosis is lower.
- The hemoglobin level in the body should be above 12mg/l
- The stage of cancer should be I or II
- Fewer than 4 lymph nodes should be affected
References:
- Prognostic factors versus predictive factors: Examples from a clinical trial of erlotinib - (http://www.moloncol.org/article/S1574-7891(07)00102-0/abstract)
- Molecular Pathology Testing To Estimate Prognosis for Common Cancers - (https://www.cms.gov/Regulations-and-Guidance/Guidance/FACA/downloads/id69b.pdf)
- Survival rates and factors that affect prognosis (outlook) for non-Hodgkin lymphoma - (http://www.cancer.org/cancer/non-hodgkinlymphoma/detailedguide/non-hodgkin-lymphoma-factors-prognosis)
- Head and Neck Cancers - (https://www.cancer.gov/types/head-and-neck/head-neck-fact-sheet)