Hydroxychloroquine used for treating newly diagnosed rheumatoid arthritis (RA) shows a significantly lower risk of developing chronic kidney disease (CKD) compared with non-users when used for long-term.
- Hydroxychloroquine, a widely used disease modifying anti-rheumatic drug (DMARD) prescribed to reduce the pain and swelling in rheumatoid arthritis
- Patients with newly diagnosed rheumatoid arthritis were studied for the long-term effects of hydroxychloroquine
- Incident of chronic kidney disease was found to be low in patients who took hydroxychloroquine when compared with hydroxychloroquine non-users.
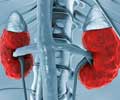
Risk of Chronic Kidney Disease in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients
Hydroxychloroquine, is one of the widely used drugs to treat rheumatoid arthritis. However, the documentation of long-term effects of hydroxychloroquine was lacking in meeting these criteria; a study was conducted by Prof. Der-Cherng Tarng and his team. The study was an observational cohort study involving nearly 2619 patients with the newly diagnosed rheumatoid arthritis condition. These patients were enrolled in Taiwan’s National Health Insurance Research Database between January 1, 2000 and December 31, 2013. The team investigated the association of hydroxychloroquine use with incident chronic kidney using a method called multivariable Cox proportional hazard regression. The total 2619 patients who were newly diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis were divided into two categories such as hydroxychloroquine users and hydroxychloroquine non-users. The group involving 1212 patients were given hydroxychloroquine, while the other group of 1407 patients was not given hydroxychloroquine. The incident of chronic kidney disease was reported by the patients who belonged to both the groups. However, the team used the method of multivariable adjustment for investigating the association of hydroxychloroquine use with incident CKD in both the groups.Prof. Der-Cherng Tarng and his team concluded their large-scale study with the findings that the risk of the incident CKD was lower in the group of hydroxychloroquine users when the results were compared with hydroxychloroquine non-users.
What are the Common Side Effects of Hydroxychloroquine?
- Vision disturbances
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Loss of appetite
- Indigestion
- Stomach pain
- Muscle weakness
- Headache
- Skin rashes or acne
- Ringing sensation in the ears
- Hair loss
- Mouth blisters
- Worsening of existing psoriasis and porphyria
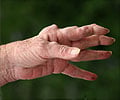
What is rheumatoid arthritis?
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease associated with the symptoms of pain, swelling, and stiffness of the joints which usually affects the wrists, hands, and feet. The effects on the joints will be symmetrical which means both the joints are affected simultaneously. Rheumatoid arthritis is also called as a systemic disease as it may affect other body systems such as respiratory or cardiovascular symptoms.Women are considered to be three times more vulnerable in acquiring the disease than men. Men are affected later if life, while women are affected between the age of 30 and 60.
How do you treat rheumatoid arthritis?
- physiotherapy
- Occupational therapy
- Surgery to correct joint symptoms
- drugs
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (e.g., Ibuprofen, Ketoprofen, Naproxen)
- Corticosteroids (e.g., Prednisolone, methylprednisolone)
- Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (e.g., Hydroxychloroquine, methotrexate, sulfasalazine)
- JAK inhibitors (e.g., Tofacitinib)
References:
- Hydroxychloroquine Use and Risk of CKD in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis - (http://cjasn.asnjournals.org/content/early/2018/04/15/CJN.11781017.abstract)
- What are the possible risks and side-effects of hydroxychloroquine? - (https://www.arthritisresearchuk.org/arthritis-information/drugs/hydroxychloroquine/possible-side-effects.aspx)
- What is Rheumatoid Arthritis? - (https://www.arthritis.org/about-arthritis/types/rheumatoid-arthritis/what-is-rheumatoid-arthritis.php)
- Rheumatoid arthritis- overview - (https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/rheumatoid-arthritis/)
Source-Medindia