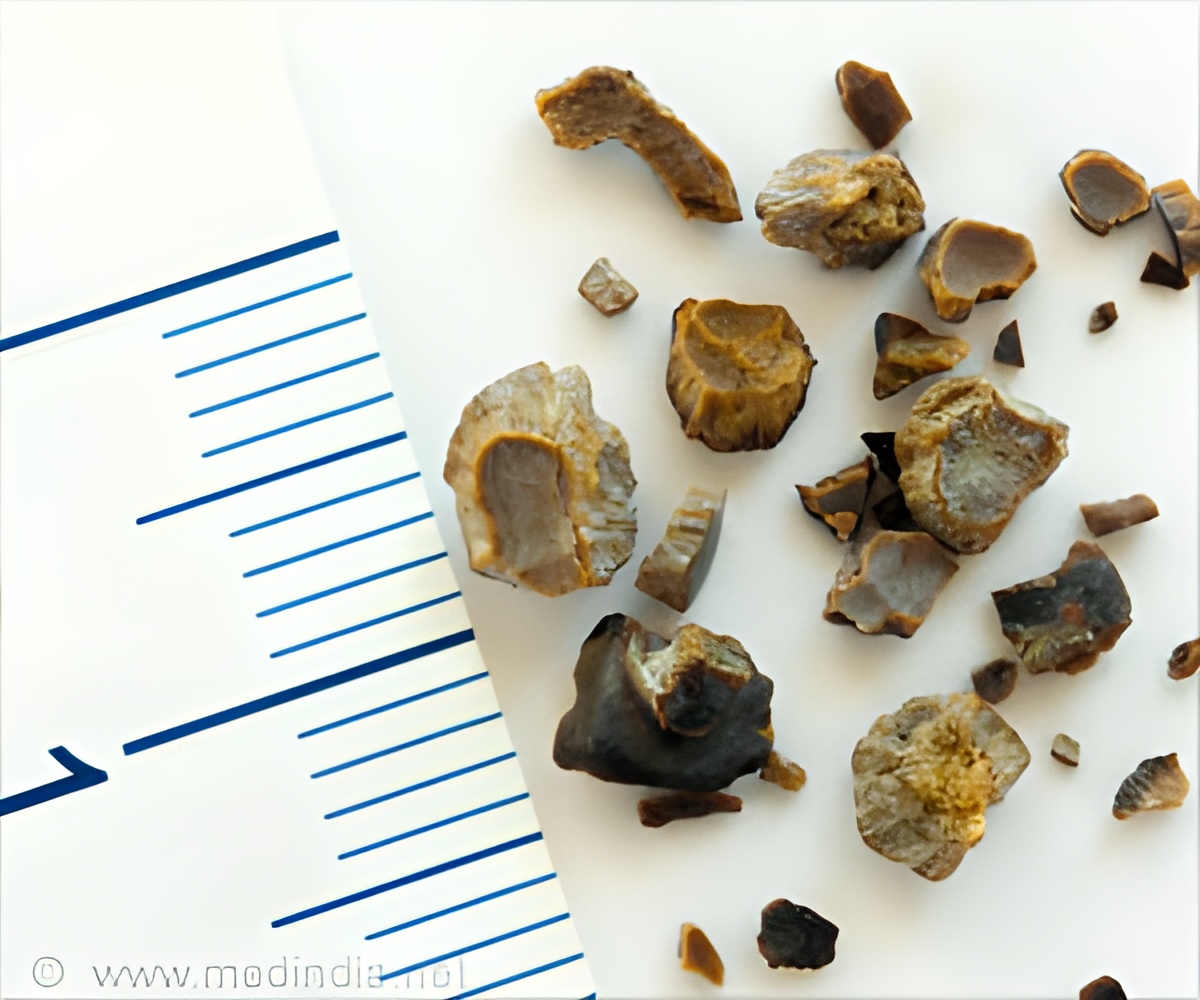
The incidence of kidney stones is increasing considerably with a significant increase among adolescents, prompting swift action to control risk factors.

- Children
- Adolescents
- Females
- Blacks
Highlights of the study:
- 153,000 pediatric, as well as adult patients, were treated for kidney stones between 1997-2012.
- Annual incidence- increased by 16%.
- Largest incidence among 15 to 19-year-olds.
- The childhood cumulative risk for kidney stones was more or less the same for both boys as well as girls.
- Girls(87%)
- Boys (90%)
- The lifetime risk for kidney stones increased for women while it remained constant for men.
- Women - 10.5% to 15.2% increase
- Men- 23%
- Incidence of kidney stone based on race showed that there was significant increase among blacks when compared with whites.
- Blacks- 15%
- Whites- 3%
Reason Behind the High Incidence of Kidney Stone
The increase in the incidence of kidney stones is a worrying factor, but it is important to identify underlying factors that contribute to the increased incidence.
Dr. Clarke, an expert on kidney stones states that the increased incidence could be due to,
- Obesity
- Increased incidence of diabetes
- Increased intake of food high in sodium
- Dehydration
In the paper, the scientists argue that genetic and environmental factors are the causes for kidney stone formation. However, a significant genetic change triggering the high incidence of kidney stones is unlikely and it is largely due to dietary habits and global warming.
- Increased consumption of corn and corn starch food
- Increased consumption of fructose-rich foods
- Decreased intake of Calcium and fluid
- Increased Oxalate consumption
- Increased intake of animal protein
The increase in global temperature as a result of global warming has also been found to increase incidence of kidney stones. This was first brought to the fore when considerable American soldiers posted in Kuwait between 2002 and 2004 developed kidney stones.
The risk for kidney stones will increase from 40% in 2000 to 56% in 2050 and then up to 70% in 2095.
Dr. Scales believes that kidney stones may foreshadow medical conditions that may occur in the future like chronic kidney disease, heart diseases and bone density loss. This necessitates better screening procedures and the need to bring about lifestyle, dietary changes and home remedies that can limit the risk for kidney stones.
References:
1. http://www.the-hospitalist.org/article/12856/
2. Victoriano Romero, Haluk Akpinar and Dean G Assimos, “Kidney Stones: A Global Picture of Prevalence, Incidence, and Associated Risk Factors” Rev Urol. 2010 Spring-Summer; 12(2-3): e86–e96
3. Brikowski TH1, Lotan Y, Pearle MS, “Climate-related increase in the prevalence of urolithiasis in the United States.” Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Jul 15
Source-Medindia