Inactivation of tumor suppressors STAG2 or STAG3 reactivates cell-growth signaling pathway in BRAF mutant melanoma.
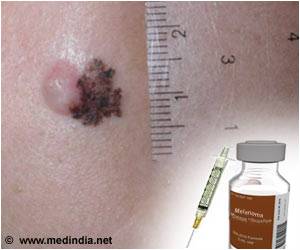
- Melanoma is the most deadly form of skin cancers
- About half the cases of malignant melanoma tumor growth are driven by mutations in the BRAF gene
- Targeted treatments with drugs usually help in suppressing tumor growth by inhibiting the activity of BRAF gene, but additional mechanism of resistance to targeted treatment for BRAF gene has been identified
- Suppressing the gene activity responsible for regulating key aspects of cell division can reactivate the signaling pathway that causes tumor growth which had been blocked by BRAF inhibitor drugs.
- Cell growth and division - Proliferation
- Cell maturation - Differentiation
- Cell movement- Migration
- Self-destruction- Apoptosis
Researchers at the Massachusetts General Hospital have identified an additional mechanism of resistance to targeted treatment for BRAF mutant melanoma. Their paper, receiving advance online publication in Nature Medicine, reports that when the mutations in two genes responsible for regulating key aspects of cell division are inactivated, the signaling pathway driving tumor growth that had been blocked by BRAF inhibitor drugs gets reactivated.
"Our finding that loss of the tumor suppressors STAG2 or STAG3 is a novel genetic mechanism of BRAF inhibitor resistance also revealed an unexpected link between those proteins and the MAPK cell-growth pathway, activation of which drives these tumors," says Bin Zheng, PhD, of the Cutaneous Biology Research Center at MGH, corresponding author of the paper. "Understanding and overcoming resistance to BRAF inhibition remains a major challenge facing the melanoma field. Identifying biomarkers capable of predicting response to BRAF inhibitor drugs - such as vemurafenib and dabrafenib - will facilitate early identification of patients likely to benefit from treatment and enable monitoring the development of resistance, which would allow consideration of other treatment options prior to relapse."
In their search for additional resistance mechanisms, a patient's tumor samples were taken before treatment and after resistance development to the BRAF inhibitor drug vemurafinib. Investigators then performed whole-exome sequencing. They then compared the novel mutations in the post-resistance sample with a list of known cancer-associated mutations and identified a single significant mutation in the tumor suppressor gene STAG2. STAG2 and related genes called STAG1 and STAG3 code for sub-units of the cohesin complex. This assembly of proteins regulates an essential stage in cellular division (the separation of chromosomes) and plays a role in the regulation of gene expression. Mutations of several of these cohesin complex genes, including STAG2, are seen in other forms of cancer. How exactly the proteins account for their tumor suppressor functions in any type of cancer has yet to be determined.
In a panel of treatment-resistant melanoma cells, examination of all three STAG proteins, revealed a reduced expression of STAG2 and STAG3 in several cell lines, including some that were resistant to inhibition of both BRAF and of MEK, another protein in the MAPK pathway. They identified what possible could be the STAG2 mutation, but they could not find any STAG3 mutation in their panel. STAG3 mutations were identified in pre-treatment samples of tumors that soon developed resistance to treatment after examining data from previously published study of BRAF inhibitor treatment.
Experiments in cultured melanoma cell lines and in tumors implanted into mice revealed that suppression of STAG2 or STAG3 activity, reactivated the later stage MAPK pathway driving tumor growth that had been blocked by BRAF inhibitor drugs. In contrast, increasing the expression of either STAG2 or STAG3 in BRAF-mutated melanoma cells increased the effectiveness of targeted therapies using drugs line vemurafinib.
References:
- What is Melanoma? - (http://www.skincancer.org/skin-cancer-information/melanoma)
- Targeted Therapy for Melanoma Skin Cancer - (http://www.cancer.org/cancer/skincancer-melanoma/detailedguide/melanoma-skin-cancer-treating-targeted-therapy)