Current acellular pertussis vaccine in Canada is effective only for 3 years with complete loss of protection 7 years after vaccination, found researchers.
Highlights
- Researchers from the University of Toronto carried out a study to understand the effectiveness of acellular pertussis vaccine.
- The vaccine lowered incidence of pertussis in Canada
- The immunity provided by the vaccine lasts only for a period of 3 years with loss of immunity after 7 years.
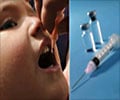
The Pertussis Vaccine
The pertussis vaccine is an acellular vaccine, as it does not contain the full organism, and is used to protect against a bacterial infection that is spread by coughing or sneezing.
The current vaccine has been used in Canada since 1997 and also used in other countries like Australia, New Zealand, Europe and North America. It is administered to children, teenagers, infants and adults to prevent the incidence of pertussis.
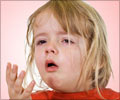
Symptoms of Pertussis
Pertussis is also called the whooping cough because of the characteristic whoop that is heard when the patient coughs. The initial symptoms include
- Mild fever
- Low grade runny nose
- Occasional cough
- Exhaustion
- Nausea and vomiting
- Characteristic whoop during persistent cough
- At 60 days after birth
- At 120 days after birth
- At 180 days after birth
- Between 1 year 3 months to 1 and a half years.
- Between 4 to 6 years
Decrease in Disease Incidence after Pertussis Vaccine
- The incidence of pertussis prior to Canada’s vaccination program was 156 cases per 100 000 people.
- After the vaccination program had started, the incidence lowered to 2 per 100 000 in 2011 to 13.9 in 2012.
Study on Effectiveness of Pertussis Vaccine
The researchers studied 5867 people between the years between 1992 to 2013. Out of which- 486 tested positive for the presence of pertussis
- 5381 were negative for pertussis
- Up to 3 years after vaccination, there was immunity against the infection.
- 7 years after vaccination, there was little immunity.
- The risk of getting pertussis increased by 27% every year.
The researchers of the study conclude by saying “… our finding that the low-effectiveness whole-cell vaccine is still better for priming than the currently used acellular vaccine nearly 2 decades after the change in practice has profound implications for understanding the effectiveness of the pertussis vaccine.”
Canada changed from using the whole organism vaccine to the acellular vaccine due to poor effectiveness of the whole organism vaccine that was used earlier. However, newer whole organism vaccines that are available in the market are found to be effective.
The results of this study are supported by other studies conducted in The United States and in The U.K that have shown a decreased immunity over a period of time.
Corrective Measures
The lack of immunity after a period of 7 years is an alarming fact in the fight against pertussis. The optimum level of immunity can be maintained by
- Vaccinating pregnant women.
- Re-immunizing children after 7 years.
- Re-immunizing when going to pertussis prone areas.
References:
- Pertussis (Whooping Cough) Vaccine - (http://www.vaccines.gov/diseases/pertussis/)
- Pertussis (Whooping Cough) - Signs and Symptoms - (http://www.cdc.gov/pertussis/about/signs-symptoms.html)