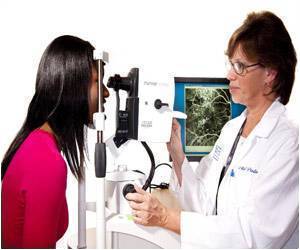
Optical coherence tomography(OCT) is an evolving method of imaging in ophthalmology. OCT is similar to ultrasound; ultrasound uses sound while OCT uses light.
What is Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT)?
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is an evolving method of imaging in ophthalmology. OCT is similar to ultrasound; ultrasound uses sound while OCT uses light. OCT can be used to detect a range of eye problems causing blindness like glaucoma, macular degeneration, diabetic retinopathy and retinitis pigmentosa.While OCT provides only structural information, speckle variance optical coherence tomography (svOCT) also provides information on blood flow. svOCT is advantageous because it provides a display of blood vessels and enables clear visualization of optical vasculature.
Retinal Angiography with Real-Time Speckle Variance Optical Coherence Tomography
Retinal capillary networks or the blood vessels in the inner layer of the eye are critical in understanding optical diseases. Accurate in vivo imaging of retinal capillary networks is desirable to understand the mechanisms of retinal homeostasis and retinal diseases. svOCT is believed to provide high quality imaging and information on retinal circulation.In the recently published study, researchers describe the method as well as compare it with other available methods.
The svOCT system uses a customized swept source OCT operating at a line rate of 100 kHz. Real-time processing and visualization was made available on a consumer-grade graphics processing unit.
To compare the quality of microvascular details acquired with svOCT, the researchers compared images of within human retinal capillary networks captured with both svOCT and fluorescein angiography. Fluorescein angiography uses a special dye and camera to examine blood flow in the retina and choroid which are the two layers in the back of the eye. They found that the microvascular details captured with svOCT had better density as compared to fluorescein angiography.
The researchers found that the svOCT device was able to produce en face images of capillary networks which were structurally comparable to previously published tissue studies. The researchers found that the svOCT device was able to non-invasively detect the early manifestations of diabetic retinopathy and retinal vascular occlusion.
Source-Medindia