The presence of primary cilia on retinal pigment epithelial cells is necessary for their proper structure and function in dry age-related macular degeneration.
- The presence of primary cilia on the retinal pigment epithelium appears to be essential for the cells to be structurally and functionally mature
- Stem cells treated with cilia-promoting drugs were structurally and functionally mature, and formed a monolayer
- Mutations in the cilia-promoting genes resulted in defective retinal pigment epithelial cells
On exposure of the cells to cilia-promoting drugs:
- The RPE cells formed were structurally mature and were oriented as a single functional monolayer
- Their genetic constitution resembled more of adult RPE cells
- They engulfed the photoreceptor outer segments, which reflects the proper functioning of the RPE cells
- Their cilia appeared to enhance the maturation of the cells by inhibiting the canonical WNT signaling. However, the suppression of the WNT signaling is not enough for the maturation of the RPEs, as demonstrated by further experiments and requires further PKCδ activation
- The RPE cells were immature structurally and functionally
- The RPE cell density and the polarity of the cells were altered, resulting in maturational and functional defects
- RPE cells from stem cells of patients with mutations in the cilia gene CEP290 had smaller cilia, with the resultant cells developing structural and functional defects. The lack of maturation of these cells was shown to be associated with retinal degeneration
- The study in mice demonstrated that damage to the RPE cells occurs before the damage to the photoreceptors. It also emphasized the importance of WNT suppression to ensure the maturation of the RPE cells
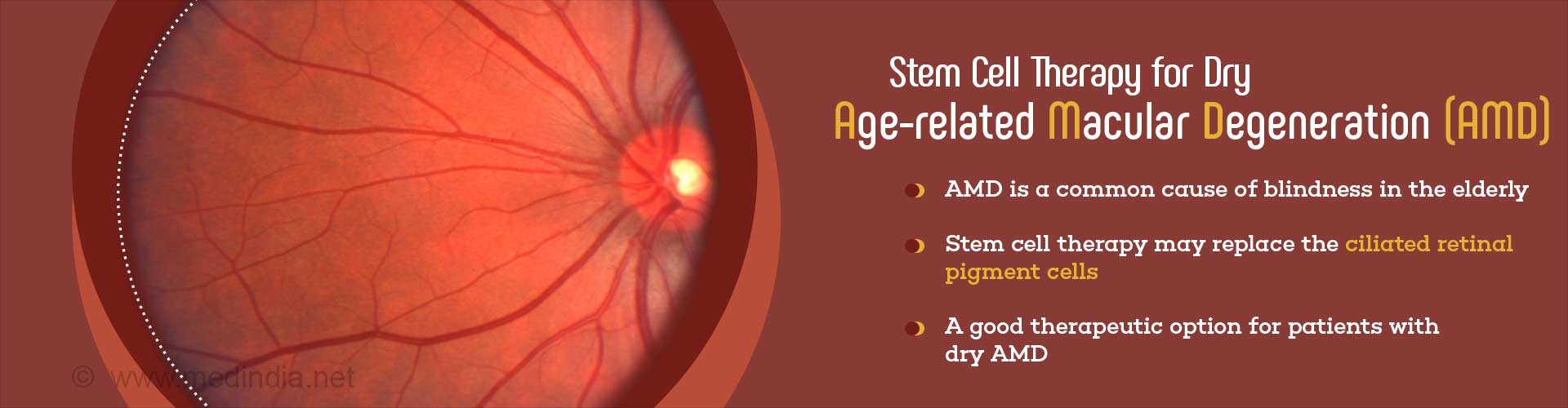
About Dry Age-related Macular Degeneration
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is a condition where the photoreceptors (light-sensitive cells) in the macula undergo degeneration, usually above the age of 50 years, resulting in blurred vision. A family history and smoking increase the risk of developing the condition. In dry age-related macular degeneration, the photoreceptors as well as the supporting tissue in the macula consisting of retinal pigment epithelial cells undergo degeneration. There is no specific treatment for the condition. Some patients may benefit from the intake of mineral and vitamin supplements. In the recent years, treatment with stem cells is being explored for the condition. However, this approach has faced some roadblocks due to the incomplete maturation of the stem cells during the studies.About the Retina
The retina is the inner light-sensitive layer of the eye. It detects the rays of light that enter the eye and converts them into electrical signals that are carried to the brain via the optic nerve. The retina contains two types of photoreceptors, the rods that detect dim light, and the cones that are responsible for colored vision. The macula is the most light-sensitive region with a maximum concentration of cones and is responsible for central vision.References:
- May-Simera, Helen Louise et al. "Primary Cilium Mediated Retinal Pigment Epithelium Maturation is Retarded in Ciliopathy Patient Cells". Cell Reports. Published online January 2, 2018. DOI:10.1016/j.celrep.2017.12.038
- Facts About Age-Related Macular Degeneration - (https://nei.nih.gov/health/maculardegen/armd_facts)