Topical therapy with blood-derived products can be used for the management of ocular surface disorders that are resistant to conventional medical treatment.
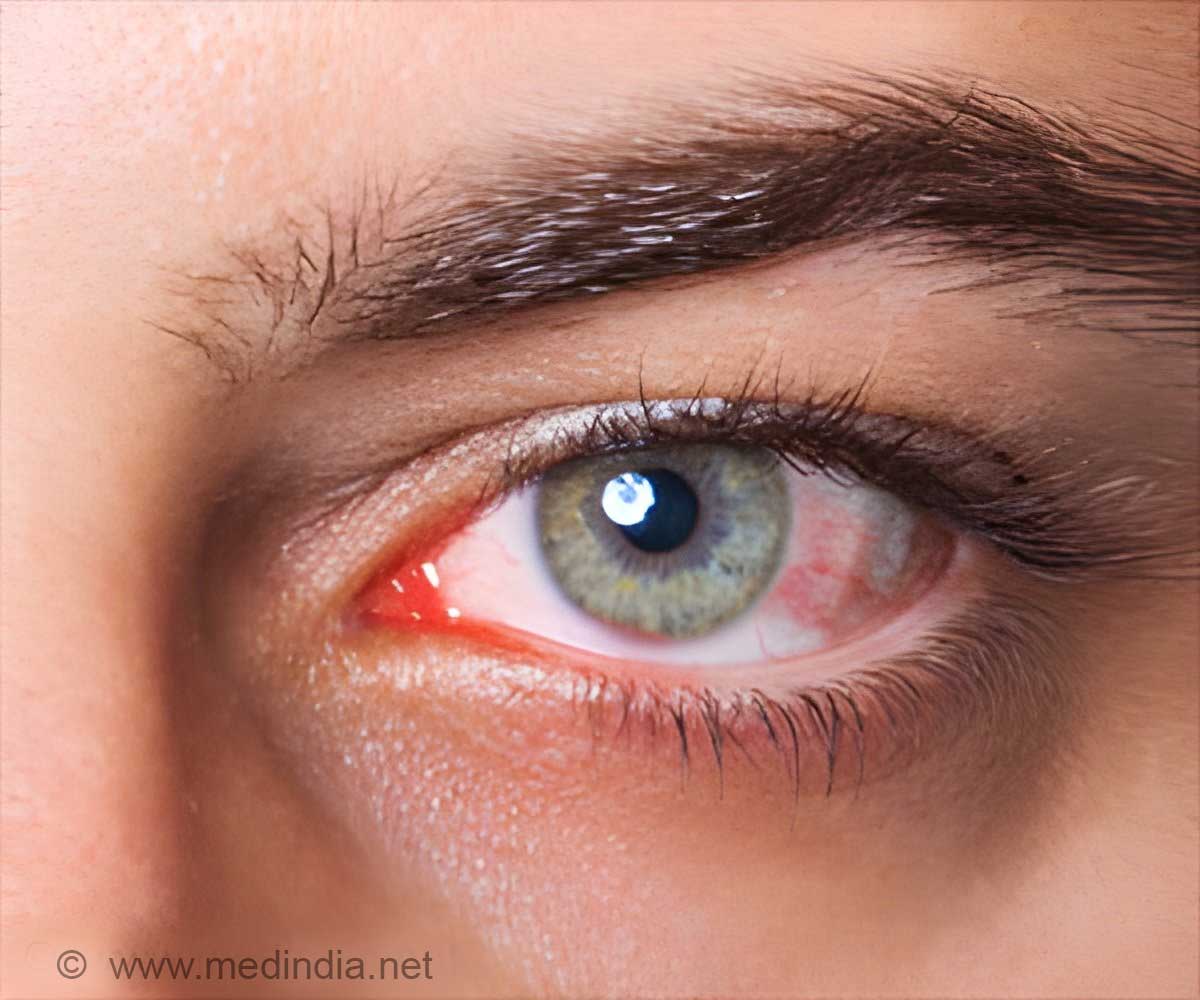
Ocular surface diseases are a group of disorders that affect the outer surface of the eye. They are caused by inflammation which are often influenced by genetic, environmental and psychosocial factors.
Patients with ocular surface diseases present with blurry vision or partial loss of vision, discomfort or pain, infection, redness, itching, erosion, ulceration and in severe cases, blindness due to scarring of the eye surface.
Artificial tear and corticosteroid eye drops are the mainstays of current treatment options for patients with ocular surface disease. However, they do have some disadvantages, which are listed below:
Disadvantages of Artificial Tear and Corticosteroid Eye Drops
- Use of corticosteroid eye drops is associated with a number of side effects.
- The commercially available artificial tear preparations do not include essential tear components such as growth factors, vitamins and immunoglobulins.
- Another drawback of using artificial tears is the fact that they often contain preservatives, stabilizers and other additives, which can result in potentially toxic or allergic reactions.
- Despite the intensive use of artificial tear supplements, many patients still present with persistent symptoms and signs of ocular surface disorders. Such patients may have more serious form of the disease with significant visual impairment and disability. Surgical interventions may be necessary in such cases.
Experts recommend using these blood-derived therapies for the management of ocular surface disorders that are resistant to usual medical treatment. However, their use is limited by the cost and the inconvenient process of obtaining these products.
Autologous serum tears have been used for the treatment of chronic dry eye syndrome for many years. Serum is the fluid component of blood that remains after clotting. It is not a standard blood product, but can easily be produced on special request to the blood bank. Autologous serum is serum that is obtained from blood withdrawn from the same patient.
Advantages of using Autologous Serum Tears
- Autologous serum tears contain essential ocular surface nutrients, such as several growth factors, vitamin A and vitamin E, fibronectin, cytokines, and bacteriostatic components also present in tears. These factors have been considered to be important for maintaining a healthy corneal and conjunctival surface.
- Laboratory studies have revealed that the ocular surface cells are better supported by autologous serum than by pharmaceutical lubricants.
- The autologous serum eye drops can offer both lubricant and nutrient properties, and can be produced without the use of any preservatives. Thus, toxicity due to additives is not an issue with autologous serum tears.
Possible side effects of autologous serum eye drops include:
- Worsening or reoccurrence of the initial problem: In some cases the ocular surface disease is likely to recur if the serum treatment is stopped.
- Risk of infection: The use of serum tears carries the risk of transmission of infectious diseases from the donor to other people involved in the production and application of the eye drops. There is also the risk of contamination of the dropper bottle and subsequent infections. Such complications can be largely avoided by prior testing of the donor and other labor for HIV, syphilis and hepatitis B and C. Every serum eye drop batch must also be tested for possible bacterial contamination.
- Immunological reactions: In rare cases, patients may present an inflammatory response after the application of the eye drops. Therefore, patients must be frequently monitored after the application of serum eye drops.
Several other quality controlled products derived from full blood can also be considered for the treatment of ocular surface disorders. These include platelet concentrates, umbilical cord serum or various protein fractions such as albumin.
Albumin is one of the most abundant proteins in tears. It supports surface wound healing. No complications have been observed with the use of albumin as a single compound product. An autologous blood donation is also not required for using albumin. However, symptoms of ocular surface disease do not show remarkable improvement with the use of albumin.
Umbilical cord serum can also be used as an alternative treatment for promoting corneal surface wound healing. It was found to be more effective than autologous serum to heal surface wounds. However, it is difficult to obtain umbilical cord serum and the supply is limited. Also, since it is obtained from a different person, umbilical cord serum can cause allergic reaction or infection.
References:
1. Soni NG, Jeng BH. Blood-derived topical therapy for ocular surface diseases. Br J Ophthalmol doi:10.1136/bjophthalmol-2015-3068422. Lekhanont K, Jongkhajornpong P, Choubtum L, Chuckpaiwong V. Topical 100% Serum Eye Drops for Treating Corneal Epithelial Defect after Ocular Surgery. BioMed Research International 2013, Article ID 521315, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/521315
3. Quintos GG, Campos M, Behrens A. Autologous serum for ocular surface diseases. Arq. Bras. Oftalmol. vol.71 no.6 supl.0 São Paulo Nov./Dec. 2008
4. http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S0004-27492008000700010
Source-Medindia