Evidence from randomized trials reveals that an oral vitamin D supplementation added to standard asthma medication is likely to reduce severe asthma attacks.
- Asthma is a chronic lung disease characterized by recurrent attacks of breathlessness and wheezing.
- Low vitamin D levels have been linked to increased asthma attacks.
- Vitamin D supplementation in addition to standard asthma treatment reduced the risk of severe asthma.
Asthma is a disease condition that affects the airways. The disease is often associated with breathlessness and wheezing that occur at recurrent intervals and vary in frequency and severity. It attacks all age groups but often starts in childhood.
- Around the world, it is estimated that 300 million people suffer from asthma, by the year 2025 this figure may rise to 400 million.
- In India, rough estimates indicate a prevalence of between 10% and 15% in 5-11-year old children.
- World-wide, the economic costs associated with asthma are estimated to exceed those of tuberculosis (TB) and HIV/AIDS combined.
- The burden of the disease is worrying and WHO experts are struggling to understand why rates world-wide are, on average, rising by 50% every decade.
The study participants were ethnically diverse, reflecting the broad range of global geographic settings, involving Canada, India, Japan, Poland, the UK, and the US The majority of people recruited to the studies had mild to moderate asthma, and a minority had severe asthma.
Most people continued to take their usual asthma medication while participating in the studies. The studies lasted for between six and 12 months.
Study Findings
- An oral vitamin D supplementation reduced the risk of severe asthma attacks requiring hospital admission or emergency department attendance from 6% to around 3%.
- Vitamin D supplementation reduced the rate of asthma attacks needing treatment with steroid tablets from 0.44 to 0.28 attacks per person per year.
- But vitamin D did not improve lung function or day-to-day asthma symptoms.
- There was no increase in the risk of side effects at doses of the vitamin D that were tested.
He also warned against taking vitamin D without advice.
More About Vitamin D
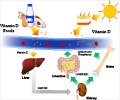
- Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin that is naturally present in foods like fish oil, fatty fish, mushrooms, egg yolks.
- When ultraviolet rays of the sun strike the skin, vitamin D synthesis in our body begins, this is our source of vitamin D and hence the name “sunshine vitamin”.
- It is also available as a dietary supplement or as Vitamin D fortified food products such as cereals, juice and milk.
- Vitamin D promotes calcium absorption and prevents rickets (softening and weakening of bones in children) in children, while preventing osteoporosis and osteomalacia in adults.
- It also helps in cell growth, neuromuscular and immunological function
- Serum concentration of 25(OH)D is the best indicator of vitamin D status.
Reference
- Vitamin D - (https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/VitaminD-HealthProfessional/)