Coronary heart disease is defined as ‘the narrowing of the small blood vessels. The study revealed that cardiovascular risk assessment could minimize the risk of cardiac ailments.
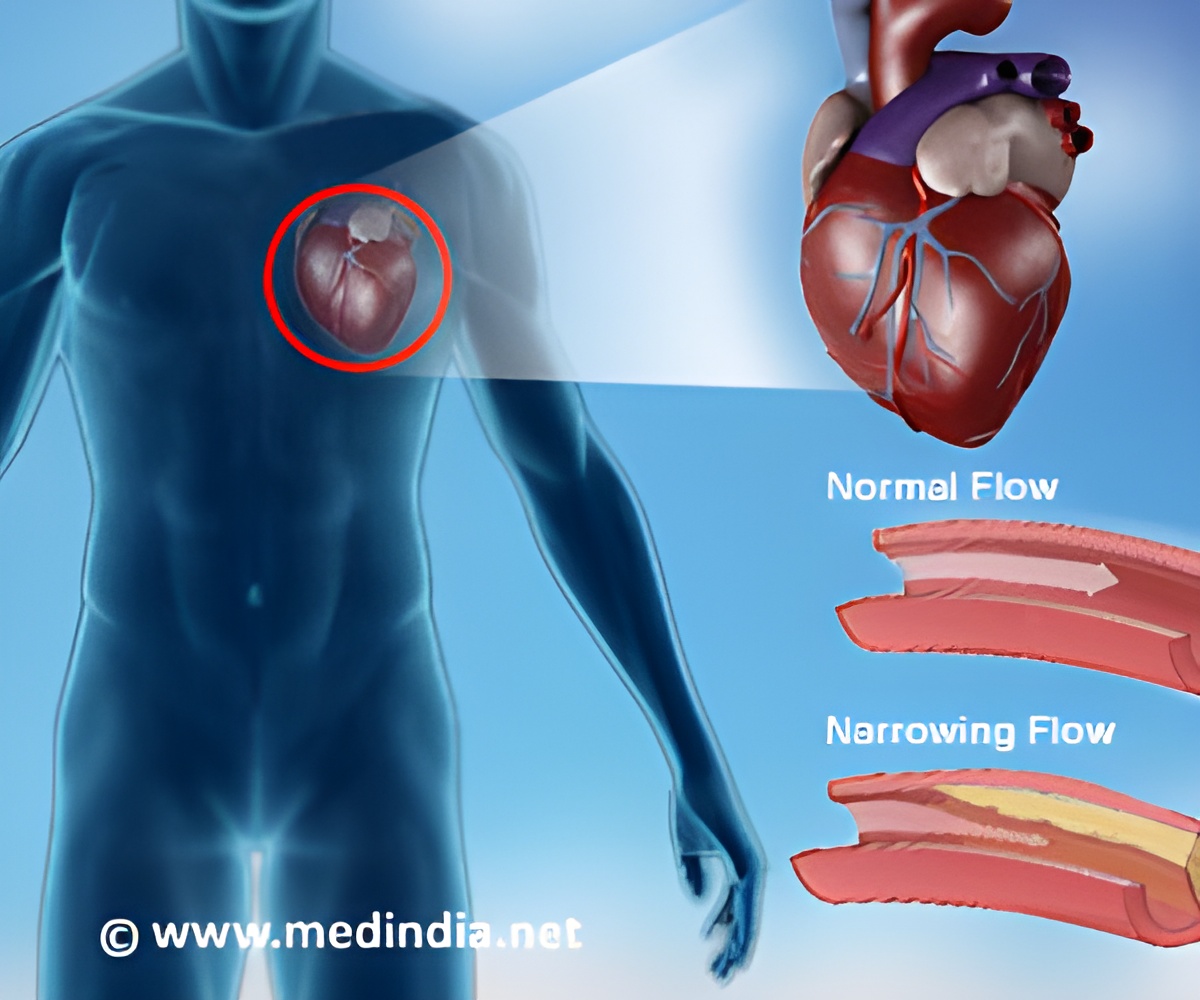
The plaque is formed by the fatty materials that get deposited on the inner walls of the arteries. Coronary arteries carry blood and oxygen to heart. These arteries become narrow due to the deposition of the plaque. This hampers the blood flow to the heart and can result in serious implications.
Primary care has an important role in the cardiovascular risk management (CVRM). Jan Van Lieshout and colleagues observed cardiovascular risk management (CVRM) in coronary heart patients and their study was published in BMC family Practices 2012.
They conducted an observational study across eight nations and collected data of patients with primary care practices from their electronic records. Records from 2960 CHD patients were collected.
‘Cardiovascular risk management (CVRM) was measured on the basis of internationally validated quality indicators.’
The experts performed analysis on the basis of multilevel regression that controlled patient’s sex and age.
The rates of risk factor for physical activity were found to be 55 percent, 94 percent for blood pressure. ‘Rates for reaching treatment targets for systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure and LDL cholesterol were 46% (sd 21%), 86% (sd 12%) and 48% (sd 22%) respectively. Rates for providing recommended cholesterol lowering and antiplatelet drugs were around 80% and 70% received influenza vaccination.’
Reference: Cardiovascular risk management in patients with coronary heart disease in primary care: variation across countries and practices. an observational study based on quality indicators; Jan Van Lieshout et al; BMC Family Practice 2012.
Source-Medindia