Blood stored longer may be less safe for patients with massive blood loss and shock as transfusion with such older stored RBCs increases the severity of bacterial pneumonia. This finding calls for improvement in the safety of stored red blood cell transfusions.
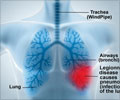
- Blood transfusion with old stored blood increases risk of lung infection.
- One such infection is bacterial pneumonia.
- Transfusion with old stored blood is also associated with dysfunction in blood flow, increased injury, and inflammation in critical organs.
Blood transfusion using red blood cells that have been stored for a long time has adverse effects, research at the University of Alabama at Birmingham finds. For severely injured patients who have massive bleeding and receive many transfusion units, older blood was associated with dysfunction in blood flow, increased injury and inflammation in critical end organs, and lung infection.
This may reveal new approaches to improve the safety of stored red blood cell transfusions.
What causes infection in blood transfusion with old stored blood?
The key player is free heme, a breakdown product from degraded red blood cells. Heme is part of the oxygen-binding hemoglobin pigment that gives blood cells their red color and carries oxygen through the body from the lungs. While in the red blood cell, heme is relatively safe; but once outside the confines of the red cells, free heme is toxic and can cause tissue injury. During storage and upon transfusion, stored red blood cells lyse open, releasing free heme.
An adverse role for heme suggests that finding ways to limit heme exposure or prevent heme toxicity may improve the safety of stored red blood cell transfusions, say UAB researchers Rakesh Patel, Ph.D., and Jean-Francois Pittet, M.D.
Patel is a professor of pathology and director of the Center for Free Radical Biology, and Pittet is a professor of anesthesiology and perioperative medicine at the UAB School of Medicine.
Compared to fresh blood, resuscitation with the stored blood significantly increased bacterial lung injury, as shown by higher mortality, and increases in fluid accumulation and bacterial numbers in the lungs.
A connection between free heme and infection susceptibility and severity was shown two ways. First, Pseudomonas aeruginosa-induced mortality was completely prevented by the addition of hemopexin, a scavenging protein in humans that removes free heme from the blood.
Second, adding an inhibitor of a cell surface receptor called toll-like receptor 4, or genetically removing that receptor from mice, also prevented the bacteria-induced mortality. Free heme, which is known to induce inflammatory injury to major organs in diseases like sickle cell or sepsis, acts, in part, by activating the toll-like receptor 4.
The researchers also found that transfusion with stored blood induced release of the inflammation mediator HMGB1, part of the body's immune response.
In tissue culture experiments, Patel, Pittet and colleagues found that addition of free heme increased permeability in a sheet of endothelial cells, and free heme inhibited macrophages from ingesting Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Macrophages are immune cells that remove infection by ingesting and destroying bacteria.
Finally, in a 16-month study, the researchers found that human trauma-hemorrhage patients who received large amounts of transfused blood were also receiving amounts of free heme sufficient to overwhelm the normal amounts of hemopexin found in a person's blood.
"We recognize that many challenges and questions remain and view our data as hypothesis-generating," Patel, Pittet and colleagues said. "Clinically, our findings underscore the need to establish whether the storage age of transfused red blood cells correlates with increasing levels of free heme after transfusion, and whether low ratios of hemopexin to free heme will identify patients at greater risk for adverse outcomes after massive transfusions."
References:
- https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1002522. Role of Heme in Lung Bacterial Infection after Trauma Hemorrhage and Stored Red Blood Cell Transfusion: A Preclinical Experimental Study, PLOS Medicinehttps://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1002522
Source-Eurekalert