Weight, rather than age, may be more meaningful when determining recommended doses of omega-3-fats for children.
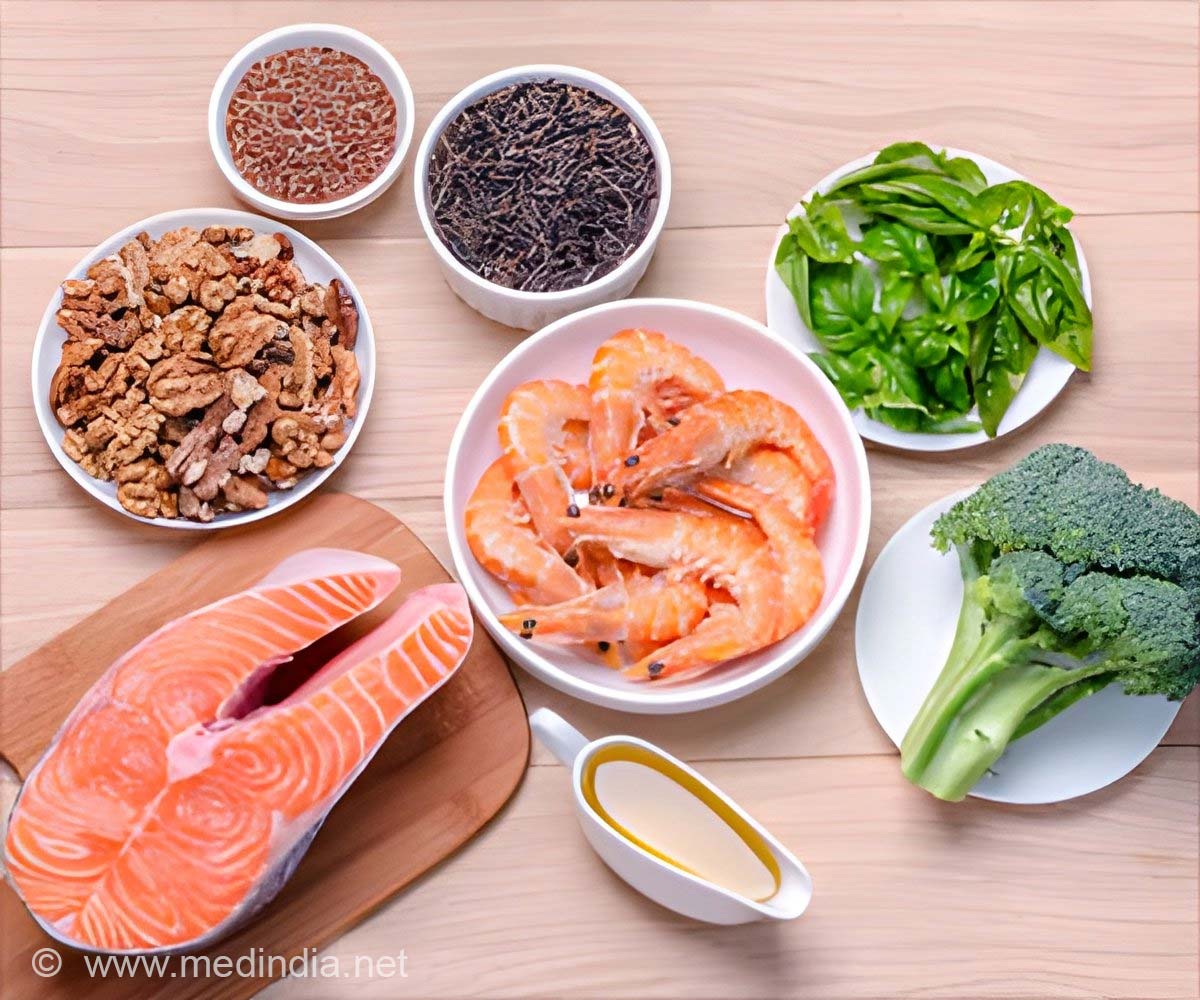

- EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid) are omega-3 fatty acids and are found naturally in foods including salmon, walnuts and soybeans.
- Omega-3 //consumption has been shown to lower blood pressure and increase good cholesterol (HDL) in children 8 to 15 years old.
- Body weight might be a good indicator to determine the dose of good fats for children. Omega-3 fats are good for the body and are mostly used as supplements but body mass index influences the benefits it offers to the body. Body weight plays a significant role in how much benefit children may get from consuming "good" fats, new research suggests.
- Lisa Christian et al., Body weight affects £s-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) accumulation in youth following supplementation in post-hoc analyses of a randomized controlled trial, PLOS One (2017) http://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0173087.
Determining the Dose of Omega-3-fats
The data comes from a trial conducted by Mary Fristad, professor of psychiatry, psychology and nutrition, and Eugene Arnold, professor emeritus of psychiatry and behavioral health. Their work looked at fatty-acid supplementation in 64 children with mood disorders.
The 7- to 14-year-old children took either an omega-3 supplement or a placebo for 12 weeks. Those who took the supplement received 2,000 milligrams of omega-3 fatty acids in the form of four capsules daily.
"We have a growing body of evidence that omega-3 fatty acids are beneficial for physical and mental health. This paper gives us more information about an important question about taking omega-3 supplements -- how much is a good amount," Fristad said of the new study.
The more a child weighed, the smaller the measurement was of two key omega-3 fatty acids in their bloodstream. And the higher the BMI category, the lower the levels of EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid).
Most of the science behind omega-3 benefits has concentrated on adults, infants and small children. But a growing body of research is looking at their role in the health of older children. In particular, omega-3 consumption has been shown to lower blood pressure and increase good cholesterol (HDL) in children 8 to 15 years old.
Omega-3 fatty acids are found naturally in foods including salmon, walnuts and soybeans. Parents looking to feed their children more of these foods should be mindful that as they gain weight they'll need more of them to make a difference, said lead author Lisa Christian, an associate professor of psychiatry in the Institute for Behavioral Medicine Research at Ohio State's Wexner Medical Center.
"While this study just looked at fatty acid supplements, it's important to recognize that weight differences could factor into how children and adults respond to many types of medications," Christian said.
"Weight, rather than age, may be more meaningful when determining recommended doses. The difference in size between a 7-year-old and a 10-year-old can be quite significant," she said.
Given fluctuations in BMI percentile measures as children grow, it would seem to make the most sense to base dosing on weight alone, Christian said.
The study also points to a need to consider weight-related differences in all studies of omega-3 intake in adults and children, the researchers wrote in their study.
Reference
Source-Medindia