The type of immune response that helps maintain healthy metabolism in fatty tissues, also drives obesity-induced nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
- Type 1 inflammation has been linked to insulin resistance in obesity, while type 2 is thought to maintain healthy metabolic signaling in fatty tissues.
- A new discovery //found that genetic predisposition towards type 1 inflammation protected mice against liver fibrosis from non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
- Type 2 inflammation in the liver could be used as clinical indicators to predict NAFLD progression.
Kevin Hart and colleagues made an unexpected discovery: that genetic predisposition towards type 1 inflammation protected mice against liver fibrosis from NAFLD following consumption of a high-fat diet.
Yet, surprisingly, Hart et al. found evidence for type 2 inflammation in biopsy samples from 56 human patients with severe liver fibrosis from NAFLD.
An anti-inflammatory therapy called TGF- ß blockade reduced markers for NAFLD-associated fibrosis in mice fed a high-fat diet, but increased type 2 inflammation in the animals' livers.
The authors say that signs of type 2 inflammation in the liver could be used as clinical indicators to predict NAFLD progression.
NAFLD is the most common type of progressive liver disease in developed countries and the second leading indication for liver transplantation.Because obesity, NAFLD, and inflammation are closely linked, ongoing efforts have attempted to develop interventions designed to modulate affected individuals' immune responses.
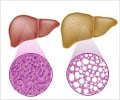
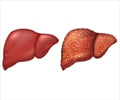
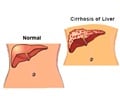
In NAFLD the excess fat accumulation is in the form of excessive triglycerides in the liver and they occupy more than 5% of liver cells called hepatocytes. This means that the fat forms 5% of the weight of the liver. Normally there is hardly any fat present in the liver.
Direct medical costs associated with NAFLD total as much as $103 billion every year in the United States, and no drugs are approved to treat the 64 million people in the nation living with the condition.
Treatment
The primary treatment for NAFLD is lifestyle modification. Eating a balanced diet, eating less, and increasing one’s physical activity all promote weight loss and improve or prevent diabetes and fatty liver.
In severe cases of obesity, surgical or minimally invasive weight loss procedures may be considered, such as gastric bypass surgery (open, laparoscopic, or robotic) or endoscopy.
Reference
- K.M. Hart et al., Type-2 immunity is protective in metabolic disease but exacerbates NAFLD, Science Translational Medicine (2017) DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aal3694.
Source-Medindia