Air pollution, exposure to mice, cockroach may worsen asthma symptoms in a person who has it but may not increase the risk of having asthma.

- Certain risk factors concentrated in urban areas, such as exposure to mice and cockroach allergens and air pollution, trigger asthma.
- Urban living does not increase the //risk for having asthma or may not cause asthma.
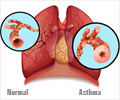
Urban Life Influences Asthma
Few previous studies have been conducted on a national level to determine the effects of inner-city living on both asthma prevalence and severity. While Keet's previous work published in 2015 using a national survey showed that living in an urban area was not a risk factor for having asthma, that study didn't allow for analysis of asthma morbidity.
The research team sought to determine those effects by analyzing information gathered by the U.S. Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services on the health care utilization of 16,860,716 children ages 5 to 19 who were enrolled in Medicaid in 2009 and 2010.
The team first narrowed the pool of data to children who had at least one asthma-related outpatient or Emergency Department visit over the two-year period. Based on the county they lived in, these 1,534,820 children were categorized by urbanization status and based on their ZIP code, categorized as living in a poor or not poor neighborhood.
Living in Cities Worsen Asthma
Keet says that, 30 percent of asthma-related hospitalizations were likely attributable to socioeconomic, geographic and/or racial/ethnic disparities; 19 percent of hospitalizations were estimated to be attributable to black race/ethnicity; 4 percent were attributable to living in a poor area; and 7 percent were attributable to living in an urban area.
Children who lived in inner-city areas had an overall 40 percent higher risk of asthma-related emergency room visits and 62 percent higher risk of asthma-related hospitalizations. After adjusting for race/ethnicity, risk was lowered to 14 percent and 30 percent higher for emergency room visits and hospitalizations, respectively.
Keet says the new study affirms her team's earlier finding that asthma rates or prevalence were not affected by residing in inner-city areas, strengthening evidence that risk factors for the cause of asthma are independent of those that worsen it. For example, exposure to pest allergens is associated with increased asthma morbidity but protects high-risk children from developing allergies.
"These results show that despite several decades of research on racial/ethnic and geographic disparities in asthma morbidity, there are still very large differences in rates of emergency room visits and hospitalizations by race and neighborhood characteristics. These findings emphasize that we need to redouble our efforts to find comprehensive solutions to address asthma disparities," concludes Keet.
The study's two main limitations were that not all states could be included because of differences in Medicaid data collection, and that it is possible that some of the differences in emergency room visits and hospitalizations could be related to how patients seek care for asthma, rather than only reflecting underlying disease severity.
Reference
- Corinne Keet et al., City living can make asthma worse for poor children, study finds, Journal of Allergy & Clinical Immunology (2017) DOI Link
Source-Medindia