Discover Delhi University's groundbreaking protein (ATH-399A) offering hope in Parkinson's treatment. Clinical trials underway in the U.S. - a potential breakthrough.
- Delhi University's ATH-399A protein enters clinical trials for Parkinson's treatment
- The unique molecule shows promise in preventing dopamine neuron death and protein aggregation
- Animal model studies and collaboration efforts pave the way for potential Parkinson's breakthrough
Parkinson's disease
Go to source).
Novel Protein Can Help Treat Parkinson's Disease
However, India has discovered a viable cure for this incurable condition, and clinical studies have begun in the United States. A unique protein discovered at Delhi University may lead to the treatment of this condition. Clinical studies for the chemical (ATM 399A) produced by Delhi University's Professor Diwan S. Rawat and Professor Kim at McLean Hospital in the United States have begun.What is Parkinson's Disease?
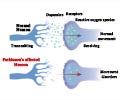
Parkinson's disease is a neurodegenerative ailment that causes tremors, stiffness, slow movements, and difficulties walking, as well as apparent behavioral disorders such as melancholy and anxiety.Causes of Parkinson's Disease
The primary cause of this disease is neuron death in the substantia nigra, which is located in the middle of the brain. This causes a lack of dopamine, and several proteins are required for the survival of dopamine neurons (2✔ ✔Trusted SourcePossible causes of Parkinson's disease
Go to source).
Clinical Trial of Novel Protein That Helps Treat Parkinson's Disease
To develop a solution for this deadly disease, researchers led by Rawat have begun clinical trials for a synthesised molecule (ATH-399A). McLean Hospital in Boston, Massachusetts, is assisting in the research cooperation.Rawat said, “It has been a long journey. Creating something like this requires a tremendous amount of energy. Sometimes you lose patience because one has to overcome numerous obstacles, from obtaining research funding to filing patents and signing technology transfer agreements. However, we remained focused, and now our molecule has reached a level where we can hope for some benefits to humanity.”
In 2021, Delhi University and McLean Hospital reached an agreement to develop this chemical with NurrOn Pharmaceuticals as a partner. Later, HanAll BioPharma and Daewoong Pharmaceutical teamed up with NurrOn Pharmaceuticals to provide the first dose to a human subject in Phase 1 clinical research.
The Phase 1 research includes healthy adults aged 18 to 80 who are given oral dosages of ATH-399A to evaluate safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics, and food effects. The study has two groups: single ascending dose (SAD) and multiple ascending dose (MAD). The first results of ATH-399A Phase 1 clinical studies are expected in the second half of 2024. The Michael J. Fox Foundation for Parkinson's Research (MJFF) is funding Phase 1 clinical trials of ATH-399A.
Preventing the Progression of Parkinson's Disease
Animal model studies have indicated that this chemical activates the critical Nur1 enzyme, preventing the death of dopamine neurons and suppressing synuclein protein aggregation. This research was recently published in Nature Communications.Rawat said, “Recently, Neurone Pharmaceuticals gave a research grant of Rs. 1 crore. However, as I am currently on probation, DU rules do not permit us to enrol Ph.D. students.”
Kim from McLean Hospital approached Rawat about collaborating on the development of a chemical for Parkinson's disease treatment. Both teams have worked tirelessly since then, and Delhi University researchers have evaluated over 600 newly synthesized molecules.
References:
- Parkinson's disease - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33848468/)
- Possible causes of Parkinson's disease - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34455768/)
Source-Medindia