Depressive symptoms are the main cause for missing out a day at work or school than symptoms related to chronic sinus disease.

- Sleep disturbance, nasal obstruction, ear, facial pain and emotional function are the categories that dominate chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS).
- Of all the assessed //symptoms, depression was the reason to miss out work or school.
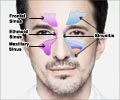
- Severe inflammation of the sinus cavities, the spaces around the cheek bones and eyes, is Chronic Sinusitis.
Link Between Depression and CRS
One of the more prevalent chronic illnesses in the United States, CRS has been known to cause significant quality of life detriments to affected patients, who often cannot breathe or sleep easily due to obstructed nasal and sinus passages.
The researchers previously identified four categories of symptoms that dominate CRS -- disturbances of sleep, nasal obstruction, ear and facial pain and emotional function. In subsequent studies, they showed that disturbed sleep and ear/facial pain are most associated with overall poorer quality of life.
In search of an association with lost productivity, the researchers assessed these four categories of symptoms in 107 patients with CRS using a standardized survey. On average, study participants reported three missed days of work or school in a three-month period, or 12 missed days in a year.
When the researchers took a closer look at the surveys, they identified emotional symptoms, in which depression symptoms are the strongest feature, as the primary driver of missed days of work or school.
The researchers were surprised to find that there was not an association between sleep disturbance or nasal obstruction symptoms--symptoms which are more commonly thought of in relation to CRS--with CRS patients missing days of work or school.
"These findings really point to the fact that specific elements (in this case, symptoms) of CRS may be driving specific disease manifestations or consequences of the disease" Dr. Sedaghat said.
Eye and Ear and assistant professor of otolaryngology at Harvard Medical School. "The severity of even symptoms most typically related to CRS, such as nasal congestion, was not associated with how often our patients missed work or school due to their CRS."
In this case, we have found that depressed mood, which CRS patients commonly experience, is associated with a particular consequence of the disease -- that patients may miss work because of CRS -- and these results open the door to exploring interventions directed at depressed mood for reducing productivity losses due to CRS."
Reference
- Ahmad R. Sedaghat et al., Depression symptoms and lost productivity in chronic rhinosinusitis, Annals of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology (2017) http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.anai.2016.12.012.
Source-Medindia