A new study suggests that consumption of artificially sweetened beverages does not significantly affect a women’s likelihood to report stress or urge incontinence.
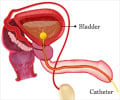
- Urinary incontinence means a person leaks urine by accident.
- While some studies in rats has shown that it is possible that artificial sweetener in drinks may have direct effects on bladder function, its effects on humans is not studied
- The amount of artificially sweetened beverage consumed was not associated with stress or urgency urinary incontinence symptoms, according to this study.
Artificially sweetened beverages and urinary incontinence-a secondary analysis of the Women's Health Initiative Observational Study
Go to source).
Artificially Sweetened Drinks and Urinary Incontinence
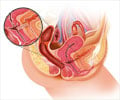
This new study, based on an analysis of data which included more than 80,000 women, specifically sought to examine the association between artificially sweetened beverages and urinary incontinence symptoms. It also aimed to identify which type of urinary incontinence—stress or urge—was most associated with beverages. The study concluded that neither stress nor urge urinary incontinence was associated with artificially sweetened beverage consumption.Urinary incontinence, defined as the loss of bladder control and the unintentional leaking of urine, is not only embarrassing, it is also associated with significant co-morbidities, including cognitive impairment, functional decline, falls, fractures, stroke, depression, and an overall poorer quality of life. It is divided into what are known as urge incontinence and stress incontinence. Stress urinary incontinence occurs when your bladder leaks urine during physical activity or exertion such as during exercise, coughing, sneezing, laughing, or lifting heavy objects. Urge incontinence occurs when someone has a strong, sudden need to urinate that is difficult to delay. The bladder then squeezes, or spasms, and they lose urine (2✔ ✔Trusted Source
Urge incontinence
Go to source).
Causes of Urinary Incontinence
Urinary tract infections, vaginal infection or irritation, or constipation can all cause incontinence. Some medications can cause temporary bladder control problems. When incontinence lasts longer, it may be due to weak bladder or pelvic floor muscles, overactive bladder muscles, damage to nerves that control the bladder from diseases such as multiple sclerosis, diabetes, or Parkinson’s disease, diseases such as arthritis that make it difficult to get to the bathroom on time, or pelvic organ prolapse, which occurs when pelvic organs shift out of their normal place into the vagina or anus. When pelvic organs are misaligned, the bladder and urethra are unable to function normally, which may result in urine leakage (3✔ ✔Trusted SourceUrinary Incontinence in Older Adults
Go to source).
The study is important because it may guide clinicians counseling women with urinary incontinence to focus more on behavioral modifications, such as total volume intake, rather than on the type of beverage consumed. Further, given the multiple potential adverse health effects associated with consuming sugar-containing beverages, counseling should be directed away from avoidance of artificially sweetened beverages.
References:
- Artificially sweetened beverages and urinary incontinence—a secondary analysis of the Women’s Health Initiative Observational Study - (https://journals.lww.com/menopausejournal/Abstract/9900/Artificially_sweetened_beverages_and_urinary.122.aspx)
- Urge incontinence - (https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/001270.htm)
- Urinary Incontinence in Older Adults - (https://www.nia.nih.gov/health/urinary-incontinence-older-adults)
Source-Medindia