AI enhances brain tumor diagnosis using DNA methylation which improving accuracy. Also AI helps in identifying new therapeutic targets with explainable AI and Random Forest models.
- AI-based tumor classification uses DNA methylation for accurate diagnosis
- The XAI framework improves tumor classification transparency
- DNA methylation patterns help in precision medicine and early cancer detection
Benfatto, S., Sill, M., Jones, D.T.W. et al. Explainable artificial intelligence of DNA methylation-based brain tumor diagnostics. Nat Commun 16, 1787 (2025)
Go to source).
AI-Based Brain Tumor Diagnosis
Traditional diagnostic methods depend on histopathology, but with recent advancements in the fields such as OMICS and machine learning (ML) has playing crucial role in analyzing genomic data and accurate tumor classification. However, the decision-making process of these ML models is not validated yet.The study developed an explainable artificial intelligence (XAI) framework designed to enhance the interpretability of DNA methylation-based brain tumor classification.
Relation between DNA Methylation and Tumor Classification
DNA methylation is an epigenetic modification that influences gene expression and plays an important role in brain tumor biology. The Heidelberg brain tumor classifier, a ML based algorithm, uses genome-wide DNA methylation profiles to categorize more than 100 genetically different brain tumor types.However, the black-box nature of ML models means that the exact reasoning behind their classifications is not always fully understood. The newly developed XAI framework aims to identify the specific DNA methylation patterns for classification decisions.
AI Framework for Brain Tumor Diagnostics
The XAI framework uses RF algorithm to analyze methylation data. RF has multiple decision trees, where each tree selects the most specific and informative features to distinguish between tumor types.By evaluating probe usage within these decision trees, it reveals critical DNA methylation regions involved in classification. Here, a "probe" is a targeted measurement—often a specific assay or short DNA sequence—that detects the methylation status at particular genomic sites, such as CpG islands. This technique allows for both global and local interpretation, identifying patterns across tumor types and specific biomarkers for each tumor class.
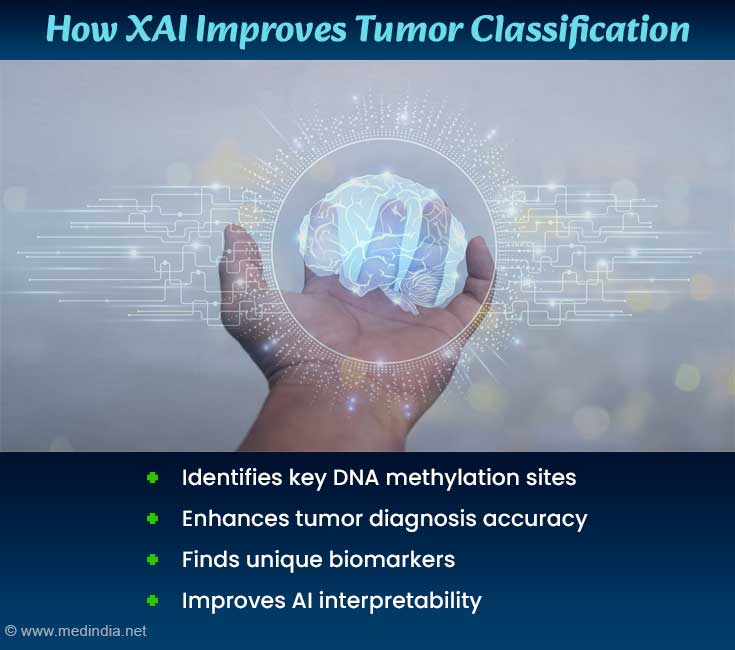
DNA Methylation: A Key to Tumor Treatment
The study found that tumors are distinguished by methylation patterns in enhancers, CpG islands, and heterochromatic domains. In this context, a "probe" is a targeted measurement used to assess the methylation status at specific genomic regions. Enhancers are regulatory elements that can boost gene expression, CpG islands are regions rich in CpG sites typically located near gene promoters, and heterochromatic domains are tightly packed segments of the genome often linked to gene silencing. These regions regulate gene expression and tumor development, making them potential targets for further study.Many genes share similar methylation patterns across different tumor classes, enhancing their accuracy and increasing the reliability of diagnoses. Understanding methylation patterns can help identify new therapeutic targets. For example, the RET oncogene is highly expressed in specific tumor classes, making it a potential target for precision medicine.
To summarize, this advanced interpretable AI framework not only improves brain tumor categorization but also lays the path for transformational applications across a broad range of malignancies, including sarcomas and meningiomas. Its versatility and precision make it a promising candidate for inclusion into liquid biopsy techniques, potentially allowing for earlier diagnosis and more effective monitoring of cancer progression, ultimately contributing to tailored treatment options and better patient outcomes..
Reference:
- Benfatto, S., Sill, M., Jones, D.T.W. et al. Explainable artificial intelligence of DNA methylation-based brain tumor diagnostics. Nat Commun 16, 1787 (2025). - (https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-57078-0)
Source-Medindia