Melanoma or aggressive skin cancer treatment using anti-PD1 is effective in some but not in many. The composition of the gut bacteria affects the treatment.
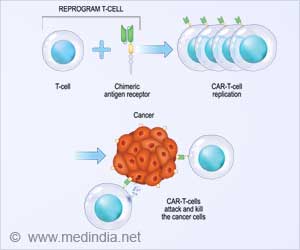
- PD1 is a protein on the surface of T cells, the immune system's specialized attack cells, that shuts down immune response.
- Anti-PD1 drugs use an antibody to block //activation of PD1.
- Anti-PD1 immunotherapy is effective for many, but not all, melanoma patients.
- Patients who responded to the immunotherapy, had a greater diversity of types of gut bacteria.
"Anti-PD1 immunotherapy is effective for many, but not all, melanoma patients and responses aren't always durable," said Jennifer Wargo, M.D., associate professor of Melanoma Medical Oncology.
"Our findings point to two potential impacts from additional research -- analyzing the diversity and composition of the microbiome to predict response to immunotherapy and modulating the gut microbiome to enhance treatment," said Wargo, senior researcher on the project.
Anti PD-1 Immunotherapy
PD1 is a protein on the surface of T cells, the immune system's specialized attack cells, that shuts down immune response. Anti-PD1 drugs use an antibody to block activation of PD1 by PD-L1, a ligand found on tumors and surrounding cells.
Gopalakrishnan, Wargo and colleagues examined oral and gut microbiome samples from 228 patients with metastatic melanoma. While no differences in response were found in connection with the oral samples, the 113 fecal samples told another story. Gopalakrishnan said the team conducted 16S rRNA sequencing, an analysis of the presence of 16S ribosomal RNA used to identify bacteria.
The researchers also conducted immune profiling before treatment for the presence of important immune system cells in the tumors. Responders had significantly increased immune infiltrates in their tumors, including the presence of CD8+ killer T cells, correlated to the abundance of a specific bacterium.
"The microbiome is highly targetable in a variety of ways," Gopalakrishnan said, including by diet, probiotics to boost the presence of helpful bacteria, antibiotics or by fecal transplants.
Reference
- Vancheswaran Gopalakrishnan et al., Gut bacteria associated with cancer immunotherapy response in melanoma, ASCO-Society for Immunotherapy in Cancer, Meeting (2017).
Source-Medindia