The risk of heart disease is higher for smokers with longer exposure to cigarettes than those who smoke more cigarettes for fewer years.

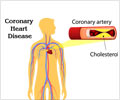
- The risk of heart disease is higher in those who smoke cigarettes over a long period of time.
- Carbon monoxide in the cigarette smoke deoxygenates blood, encourages plaque formation on arteries, over time.
Smoking accelerates the hardening and narrowing process in the arteries. It decreases HDL (good) cholesterol which help in transporting the excess fat in the blood to the liver for storage. Nicotine in the cigarette causes constriction of blood vessels which increases blood pressure resulting in hypertension. Also, smoking cigarettes increases the duration of ischemia, the inadequacy of blood supply to the heart muscles.
Acknowledging that cigarette smoking has both long-term and short-term effects on CHD, these findings suggest the long-term effects of smoking have an increased consequence. The relationship to CHD risk from smoking for a longer duration also appears to be a more widespread phenomenon than previously thought.
Reference
- Jay H. Lubin et al., New study highlights smoking intensity in coronary heart disease risk, Nicotine and Tobacco Research (2016), http://ntr.oxfordjournals.org/lookup/doi/10.1093/ntr/ntw290
Source-Medindia