Assessing the radial artery is a simple and effective way of calculating a patient’s risk for heart disease.
Highlights
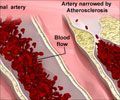
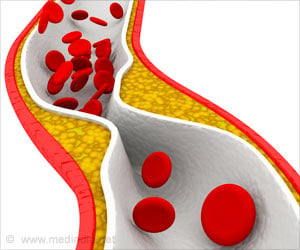
- Coronary heart diseases are on the rise and atherosclerosis is a strong indicator of heart disease.
- But there has been no accurate diagnostic tool for atherosclerosis.
- New findings state that investigating the radial artery using ultrasound could be a new way to diagnose atherosclerosis.
To grade the development of atherosclersis more accurately, a research team at New York Institute of Technology College of Osteopathic Medicine (NYITCOM) Department of Anatomy performed histopathology. This finding suggests the possibility of introducing a new way to measure systemic atherosclerosis: the radial artery.
The authors assessed the arteries of 48 cadavers to determine risk factors for atherosclerosis. They sampled 13 different arteries based on their anatomical location, including segments of carotid, central and peripheral arteries.
The central artery group included arteries that are non-palpable and commonly lead to ischemic diseases when occluded. The peripheral artery group included arteries that are accessible to palpation. The carotid artery group included branches of the carotid artery.
"It is very gratifying to combine the work perspectives of an analytical anatomist with those of a physician and a medical student to leverage synergies and discover outcomes that can be applied in a clinical setting", said Brian L. Beatty, senior author of the study.
The results showed that the radial artery, which is a peripheral vessel, exhibited a positive correlation between both the pathologic left coronary and bifurcation of the carotid arteries.
Further studies are needed to evaluate the clinical utility of radial artery ultrasonography to assess cardiovascular risk.
"Peripheral Arteries May Be Reliable Indicators of Coronary Vascular Disease," is authored by Brian L. Beatty, Ph.D., and Bennett Futterman, M.D., both associate professors of Anatomy at NYITCOM, and Christopher Hoehmann, a third-year medical student.
The study is published in The Anatomical Record.
Reference
- Brian L. Beatty et al. Peripheral Arteries May Be Reliable Indicators of Coronary Vascular Disease. The Anatomical Record; (2017) DOI: 10.1002/ar.23584
Source-Medindia