An inhalable form of oxytocin could significantly reduce the number of maternal deaths around the world, reveals study.
Highlights
- Postpartum hemorrhage (PPH) is the common cause of maternal deaths.
- Oxytocin is used for PPH treatment, however, injection requires refrigeration and skilled medical professional for administration.
- Inhalational form of oxytocin has been developed to make it easily accessible for women immediately after childbirth.
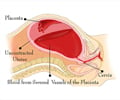
Postpartum hemorrhage (PPH) causes severe loss of blood after childbirth and is mainly responsible for maternal deaths.
The World Health Organization (WHO) has recommended the administration of oxytocin to prevent Postpartum hemorrhage (PPH). When an injection is administered, oxytocin requires refrigeration and a skilled medical professional for administering safely.
However, in low and low-middle countries, either one, or both the requirements may not be available.
Therefore, the research team in collaboration with GlaxoSmithKline in London, was developing an inhalable, dry-powder form of oxytocin.
The research study demonstrated that small-cohort study of non-pregnant female volunteers on whom the effect of the inhalational form of oxytocin was studied. This was done to compare the effects along with its injection counterpart.
Due to the positive results, the medicine may have an advantage of the streamlined pathway to registration.
Associate Professor Mcintosh, Project Leader at MIPS, said, "These results show that oxytocin can be delivered similarly via inhalation or injection and therefore we are less likely to be required to conduct the extensive and costly trials needed for an entirely new drug. Instead, we should be able to move forward with trials on a much smaller scale, featuring patients numbering in the hundreds rather than tens of thousands, potentially making the medicine available much sooner."
Further, clinical studies have to be carried out to evaluate the effects of inhaled oxytocin in women immediately after birth, to prevent postpartum hemorrhage.
Postpartum Hemorrhage (PPH)
A condition which results in excessive bleeding immediately after a childbirth is called postpartum hemorrhage.
Postpartum hemorrhage often happens within one day of giving birth and may even happen up to 12 weeks after having a baby.
It is capable of causing a severe drop in blood pressure, and if not treated quickly it may result in shock and death.
Symptoms and Signs of PPH
- Heavy bleeding from the vagina
- Decrease in blood pressure
- Pale Skin
- Swelling or pain around the vagina
Oxytocin is a hormone secreted by the pituitary gland and is produced by the hypothalamus. It is responsible for signaling the contractions of the womb during labor.
Oxytocin is given to women immediately after childbirth to prevent excessive bleeding. The drug may close the blood vessels in the placenta and helps to separate from the wall of the uterus.
References
- Postpartum hemorrhage - ( http://www.marchofdimes.org/pregnancy/postpartum-hemorrhage.aspx)
- What Does Oxytocin Do? - (http://www.hormone.org/hormones-and-health/what-do-hormones-do/oxytocin)
Source-Medindia