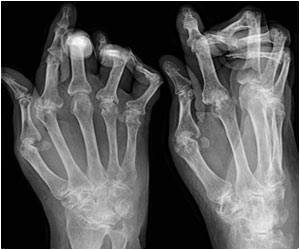
Eight of eleven genetic sites (loci) with links to osteoarthritis development, in European patients, have been identified.
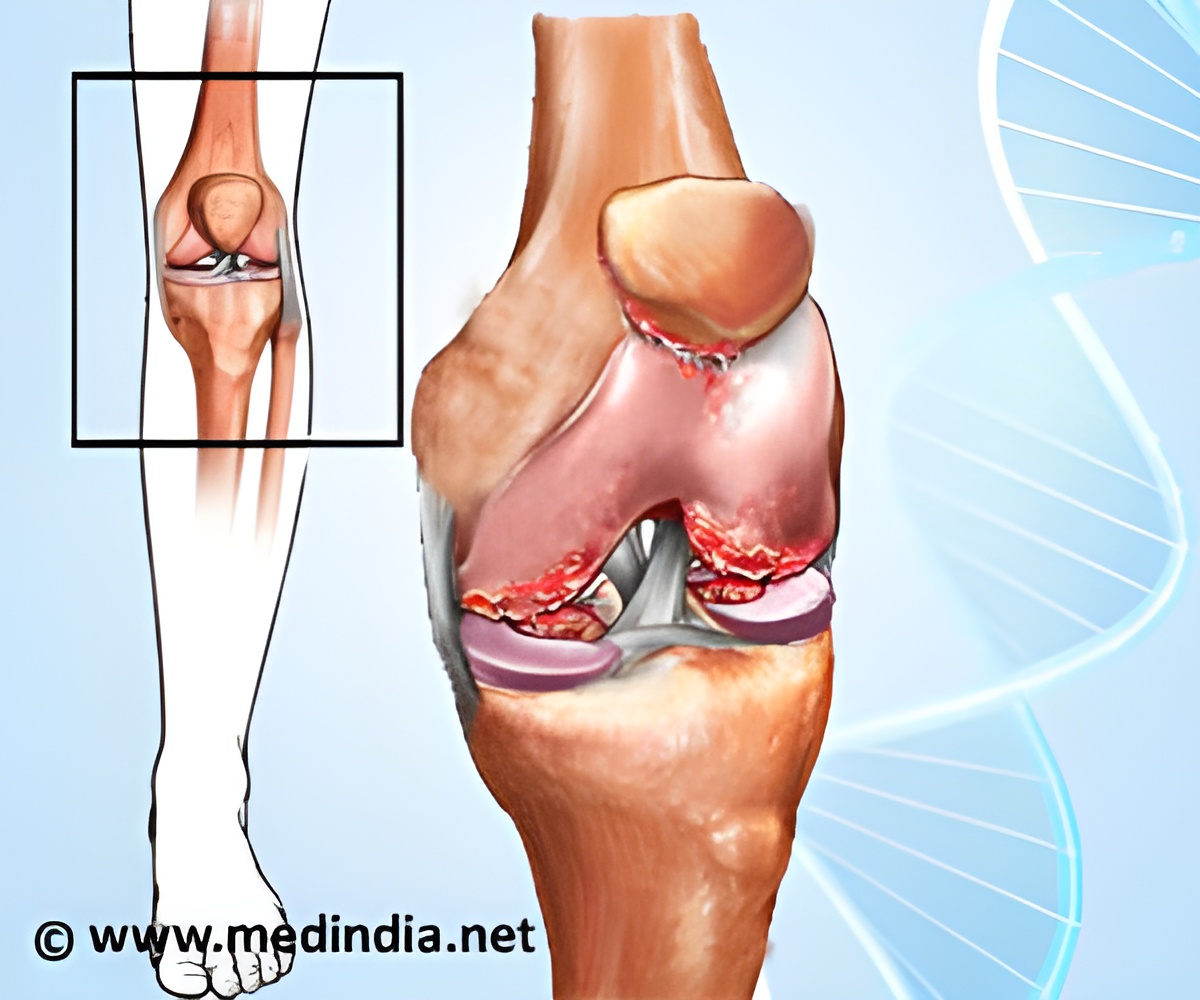
The meta-analysis identified eight genetic loci with a link to increased risk of osteoarthritis occurrence. These included rs6976 on chromosome 3, and the loci close to ASTN2 (chromosome 9), between FILIP1 and SENP6 (chromosome 6), close to KLHDC5 and PTHLH (chromosome 9), close to CHST11 (chromosome 12) and the FTO gene.
These joint-specific inherited factors do influence osteoarthritis development and progression. The association of osteoarthritis with the FTO gene (the gene related to obesity) reiterates the fact that osteoarthritis is associated with body excess weight.
Thus, the newly discovered genetic influences contribute to increased risk for osteoarthritis and provide new targets for therapeutic action.
Reference: Identification of new susceptibility loci for osteoarthritis (arcOGEN): a genome-wide association study; arcOGEN contributors; The Lancet Online Publication July 2012
Source-Medindia