Inhibiting Lysyl oxidase-like 2 enzyme which produces fibrosis of the cardiac muscle leading to heart failure could be a possible new treatment.
- In 50% heart failure cases, there is no effective treatment strategy.
- Lysyl oxidase-like 2 enzyme, is identified as the molecule that produces fibrosis of the cardiac muscle which stimulates heart failure.
- Formulating a drug which inhibits Lysyl oxidase-like 2 enzyme could be a new treatment for heart failure.
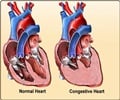
Heart Failure (HF) is characterized by a malfunction of the heart in supplying the body with enough blood for the proper working of its organs.
"This is a great challenge for society: it is the leading reason for the hospital admission of over-65's, the cause of 3% of all admissions and absorbs 2.5% of the global healthcare budget", explained Dr. Javier Díez, director of the Cardiovascular Disease Program at the Center for Applied Medical Research (CIMA) and director for Research and Innovation of the Cardiology and Cardiac Surgery Department of the Clínica Universidad de Navarra, one of the authors of this work.
The researcher points out that, "In view of this challenge, on the one hand existing healthcare resources must be optimized in order to reduce the number of new cases and improve the prognosis and quality of life of HF patients, and, on the other, to research the mechanisms that produce heart failure in order to develop treatments that are more effective and safe that the ones that exist at present".
After the activity of the enzyme is described, the next step is to develop tests for a precise diagnosis of patients with heart disease who present an excess of this molecule in their hearts. These tests will be carried out at CIMA and the Clínica Universidad de Navarra by the BIOMARCS research group, a pioneering team in the research of cardiac biomarkers for HF patients.
Reference
- Author name, Targeting LOXL2 for cardiac interstitial fibrosis and heart failure treatment, Nature Communications (2017) Doi: 10.1038/ncomms13710.