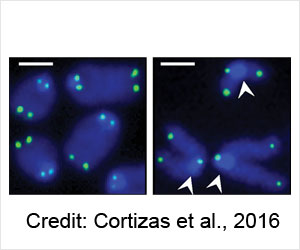
MicroRNA miR-28 plays an important role by regulating the terminal differentiation of B lymphocytes and blocking their growth.
- Aggressive forms of B cell lymphomas like Burkitt lymphoma and diffuse large cell lymphoma, often do not respond to chemotherapy and kill its victims.
- An alternative therapy using microRNA miR-28 has been discovered that helps to inhibit the growth of these B cell lymphomas.
- MicroRNA miR-28 functions by regulating the differentiation and survival of B lymphocytes, blocking the growth of these cancers.
This discovery establishes the therapeutic potential of synthetic miR-28 for inhibiting the growth of Burkitt lymphoma and diffuse large cell lymphoma and could lead to the development of the first miRNA therapy for the treatment of B cell lymphoma. This could provide the basis for human trials.
These miroRNAs (miRNAs) are small RNA molecules that regulate gene expression and has the ability to influence the biological and disease processes. The properties of miRNAs have attracted interest in their potential in the treatment of cancer.
Around 400 000 people are diagnosed with lymphoma annually, and more than 200 000 people die each year as a consequence of this type of blood cancer.
Around 60% of patients have very aggressive forms of the disease, such as Burkitt lymphoma or diffuse large cell lymphoma, and these patients often do not respond to chemotherapy or their disease relapses after treatment.
MicroRNA miR-28
The study demonstrates that miR-28 regulates the terminal differentiation and survival of B lymphocytes.
The cell differentiation plays an important role in generating memory B lymphocytes and highly specific plasma cells.
According to Dr. Ramiro, "the presence of miR-28 reduces the proliferative capacity and survival of mature B lymphocytes."
The research team discovered that miR-28 is often lost in lymphomas, and that re-establishing its expression slows tumor growth.
The study emphasizes the importance of conducting clinical trials of miR-28-based therapies to treat B cell lymphomas.
The study is published in Blood.
Reference
- Almudena R R. Ramiro et al. miR-28 regulates the germinal center reaction and blocks tumor growth in preclinical models of non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood; (2017) doi.org/10.1182/blood-2016-08-731166
Source-Medindia