New tool uncovers how brain's structural connections are unique to every individual.
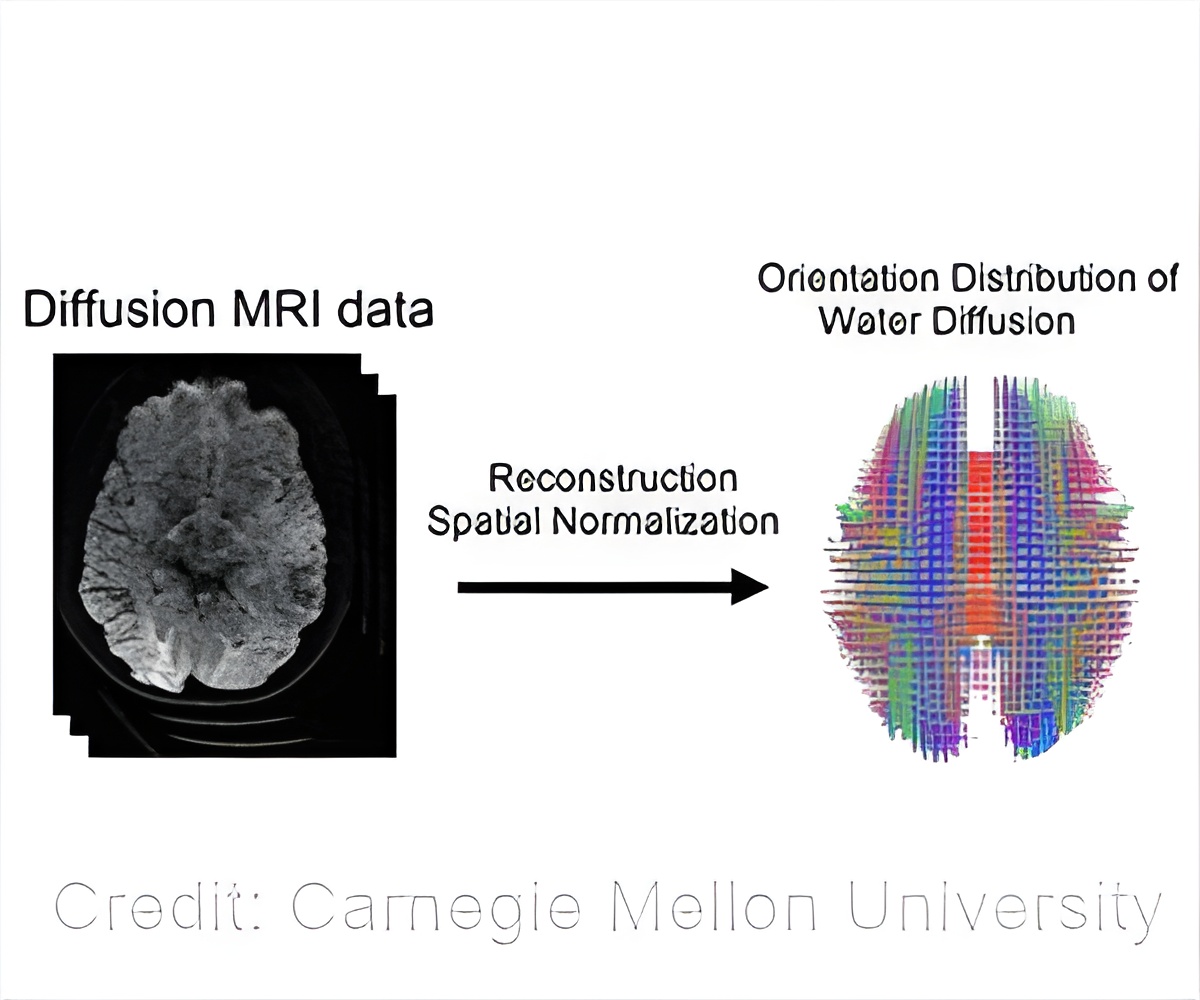
- The research team used diffusion MRI to measure the local connectome of 699 brains from five data sets.
- The new, non-invasive diffusion MRI approach captures the brain's connections at a much closer level than ever before.
- The local connectome is the point-by-point connections along all of the white matter pathways in the brain and researchers created a ‘fingerprint’ using this.
- The results showed that local connectome is highly unique to an individual.
The conventional approaches obtain a single estimate of the integrity of a single structural connection, or a white matter fiber.
The new, non-invasive diffusion MRI approach captures the brain's connections at a much closer level than ever before.
The new technique measures the integrity along each segment of the brain's biological wires, making it much more sensitive to unique patterns.
"The most exciting part is that we can apply this new method to existing data and reveal new information that is already sitting there unexplored. The higher specificity allows us to reliably study how genetic and environmental factors shape the human brain over time, thereby opening a gate to understand how the human brain functions or dysfunctions," said Fang-Cheng (Frank) Yeh, the study's first author and assistant professor of neurological surgery at the University of Pittsburgh.
For the study, the researchers used diffusion MRI to measure the local connectome of 699 brains from five data sets.
To create a fingerprint, they took the data from the diffusion MRI and reconstructed it to calculate the distribution of water diffusion along the cerebral white matter's fibers.
The measurements revealed that the local connectome is highly unique to an individual and can be used as a personal marker for human identity.
Testing the Uniqueness
To test the uniqueness, the team ran more than 17,000 identification tests.
With nearly 100% accuracy, they were able to tell whether two local connectomes, or brain "fingerprints," came from the same person or not.
Additionally, they discovered that identical twins only share about 12% of structural connectivity patterns and the brain's unique local connectome is sculpted over time, changing at an average rate of 13% every 100 days.
"This confirms something that we've always assumed in neuroscience -- that connectivity patterns in your brain are unique to you," said CMU's Timothy Verstynen, assistant professor of psychology.
"This means that many of your life experiences are somehow reflected in the connectivity of your brain. Thus we can start to look at how shared experiences, for example poverty or people who have the same patholoigical disease, are reflected in your brain connections, opening the door for potential new medical biomarkers for certain health concerns."
In addition to Yeh and Verstynen, the research team included CMU's Aarti Singh and Barnabas Poczos, the U.S. Army Research Laboratory's Jean M. Vettel, the University of California, Santa Barbara's Scott T. Grafton, the University of Pittsburgh's Kirk I. Erickson and Wen-Yih I. Tseng of the National Taiwan University.
The Army Research Laboratory funded this research.
Source-Medindia