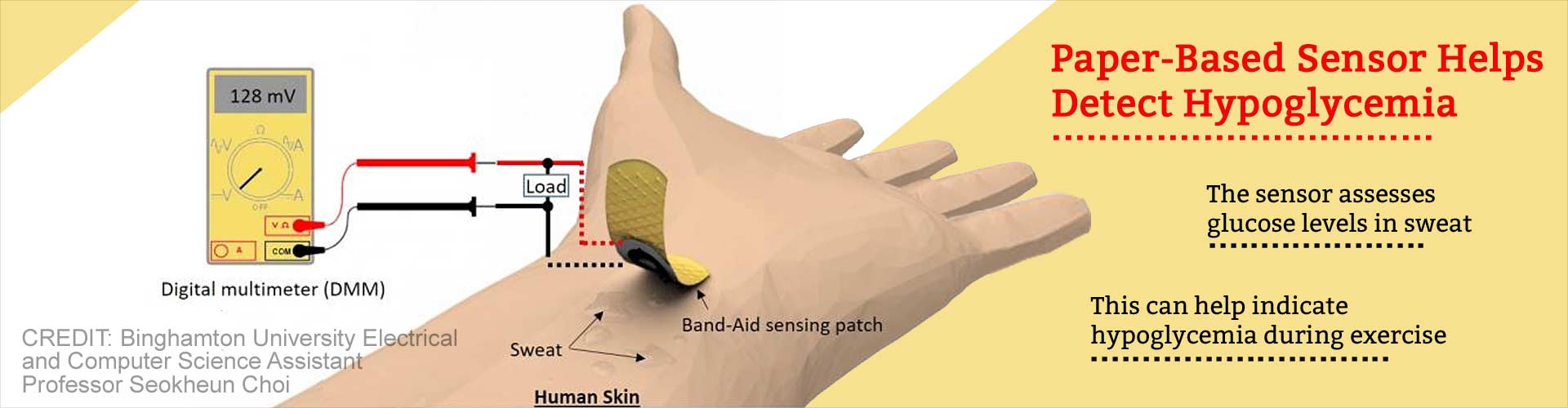
The sensor patch helps in self testing of glucose levels in the sweat and may help diabeics keep track of their blood glucose levels during exercise.
Highlights
- The newly developed paper-based sensor patch could allow diabetics to effectively measure glucose levels during exercise.
- The wearable and disposable patch allows for //non-invasive monitoring of glucose in human sweat.
- Sweat-based glucose sensing is helpful in managing exercise-induced hypoglycemia.
Exercise- Induced Hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia or low blood sugar in diabetic patients is a paradox since diabetes is characterized by high glucose levels in the blood. However, diabetics on insulin or certain oral hypoglycemic drugs and those who exercise can suffer from low blood sugar.
Normal glucose level in the body is between 70 to 110 mg/dL in a fasting state. Level below 70mg/dL is termed as hypoglycemia.
The brain depends on blood sugar as its primary source of energy, hypoglycemia interferes with the brain’s ability to function properly and can cause dizziness, headache, blurred vision, difficulty concentrating and other neurological symptoms.
Self-monitoring of Blood Glucose Levels During Exercise
- The underlying process relies on invasive and inconvenient blood sampling, causing the possibility of sample contamination and skin irritation with sweat containing various electrolytes and proteins.
- The method needs patients to carry many accessories during physical activity, including lancets, alcohol swabs and a relatively large glucometer.
- The technique requires a sophisticated electrochemical sensing technique and sufficient electrical energy, which makes the technique difficult to be fully integrated in a compact and portable fashion.
Sweat-based glucose sensing is attractive for managing exercise-induced hypoglycemia because the measurement is performed during or immediately after exercise when there is enough sweat to obtain an adequate sample, said Choi.
This potential alleviates shortcomings of conventional non-invasive sweat sensors, which can be hampered by the difficulty of collecting enough sweat for analysis, sample evaporation and the relatively long time required for sample collection.
"The sensing platform holds considerable promise for efficient diabetes management, and a fully integrated system with a simple readout can be realized toward continuous non-invasive glucose monitoring," wrote the researchers.
Reference
- Seokheun Choi et al., A Single-Use, Self-Powered, Paper-Based Sensor Patch for Detection of Exercise-Induced Hypoglycemia, Micromechanics (2017) http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/mi8090265.
Source-Medindia