According to a new Taiwanese study, people who are heavy snorers are at an increased risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis.
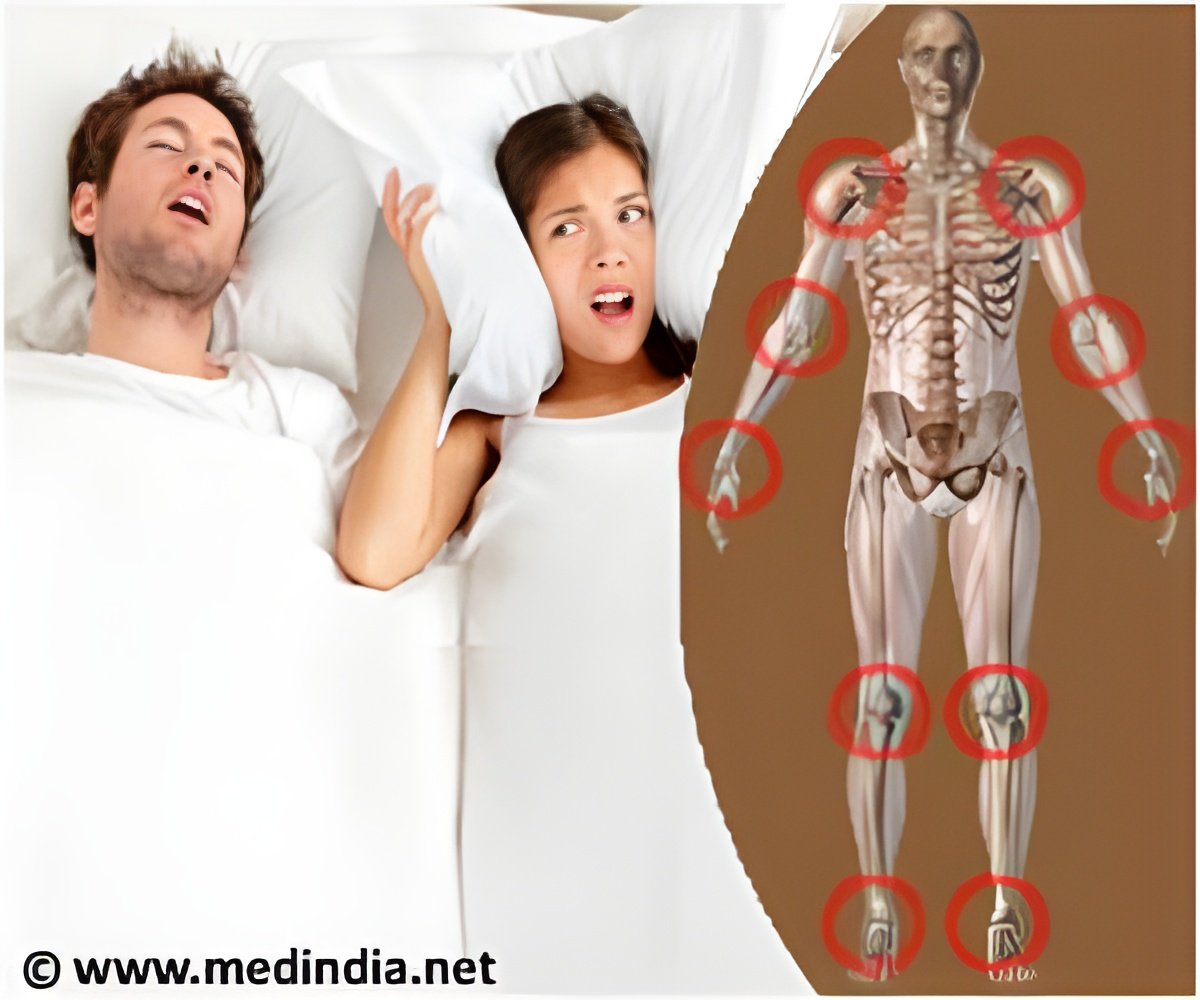
Sleep apnoea is characterized by pause in breathing while sleeping and is more common in adults than in children. The risk factors for apnoea include age, obesity, sedatives, smoking and alcohol consumption.
It has been explained that chronic sleep apnoea leads to inflammation in blood vessels present in the body and this acts as a catalyst or a trigger for the development of arthritis.
Researchers compared 1,411 sleep apnoea patients against 7,000 healthy adults for over five years. The subjects were continuously monitored for immune system related conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing, spondylitis and systemic lupus erythematous. The findings showed that the apnoea affected group had 91 percent more chances of developing any one of the three conditions.
However, the researchers pointed out that the absolute risk of falling ill was still small. "Our study is the first to investigate the association between sleep apnoea and the development of autoimmune diseases." "We think this may have gone unnoticed in clinical settings because these cases are relatively rare and may not be reported. But the potential link between the two conditions should not be overlooked”, the researchers stated in their findings.
"Among the diseases we studied, rheumatoid arthritis had the highest risk of developing in sleep apnoea patients", they said.
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic, autoimmune disorder that causes inflammation of joints and the surrounding tissues. It mostly manifests itself during middle age and is more common in women than in men. Infections, hormonal changes and genetic factors play a role in bringing about RA.
1.http://www.sleepapnoea.in/
2.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/
Source-Medindia














