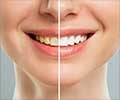
Teeth whitening is a procedure that is greatly in demand in the recent years. The procedure can be done either at home or at the doctor's office.

Superficial discoloration may be treated with scaling and polishing. Bleaching is required for stubborn stains. It is more difficult to treat dark-colored stains as compared to the lighter ones.
Teeth are whitened using hydrogen peroxide that is either directly applied, or which is released due to a reaction from sodium perborate or carbamide peroxide. Hydrogen peroxide acts as an oxidizing agent and breaks down the dark-colored stains into smaller molecules. Ammonia is also produced from carbamide, which could add to the bleaching effect.
In the case of teeth that contain fillings, crowns etc, the restorations usually do not take up the whitening, thus resulting in a contrast between the whitened teeth and the restorations. Thus, it is unwise to whiten these teeth. In addition, teeth whitening is not recommended in:
• Children less than 18 years of age
• Pregnant and lactating women
• Patients allergic to the bleaching agent
Methods of Teeth Whitening:
Teeth whitening can be done either at home using over-the-counter teeth whiteners or at the dentist’s office. At times, the dentist may apply the whitening agent and the patient can return home while the bleaching agent takes effect.
• Teeth whitening at home using over-the-counter agents: Teeth whitening at home is possible using over-the-counter products that have some bleaching action on the teeth. These products are usually milder than what the dentist uses at his clinic and therefore produce less whitening as compared to that achieved at the dentist’s office. They are effective only against surface stains. These include whitening toothpastes, strips, gels and rinses. Whitening dental floss and toothbrushes are also available. Chewing gums containing sodium hexametaphosphate have been claimed to have teeth whitening properties. In most cases, these products need a few weeks of use to bring about a noticeable effect.
• Dentist-provided bleaching: Teeth whitening can also be done with tray-based whiteners obtained from the dentist. The tray contains a bleaching agent and is worn over the affected tooth as per the dentist’s instructions. The tray that is customized by the dentist for the exact tooth produces better results with lesser side effects as compared to the trays available over the counter.
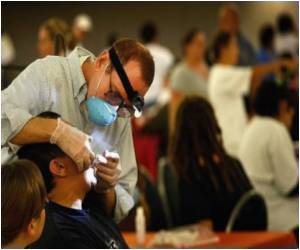
• Teeth whitening at the dentist’s office: A dentist can do teeth whitening at his office after proper evaluation of the condition. A bleaching agent is applied to the teeth, which are then exposed to heat, light or laser. The effects of this treatment are much more obvious as compared to the teeth whitening techniques used at home. Thus, though this treatment would work out to be much more expensive as compared to over-the-counter products, the chances that it would be effective with minimal side effects are more at the dentist’s office. This procedure is referred to as dentist-administered bleaching. In some cases, the dentist may place a tray with a bleaching agent in the patient’s mouth for 30 minutes to 2 hours while the patient is in the dentist’s office. This procedure is referred to as dentist-supervised bleaching.
Teeth whitening is sometimes associated with side effects. These include a temporary increase in tooth sensitivity and irritation of the gums. It is always advisable to undergo teeth whitening only after consultation and prior evaluation with a dentist. This could assure a better effect with possibly lesser side effects, even if you wish to use over-the-counter products.
Reference:
• Demarco FF, Meireles SS, Masotti AS. Over-the-counter whitening agents: a concise review. Braz Oral Res 2009;23(Spec Iss 1):64-70
• Dahl JE, Pallesen U. Tooth Bleaching - A Critical Review of the Biological Aspects. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med 2003; 14(4):292-304
Source-Medindia