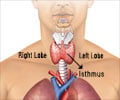
Brain–thyroid relationships are less apparent in the adult brain, though important. These are more significant in a developing brain.
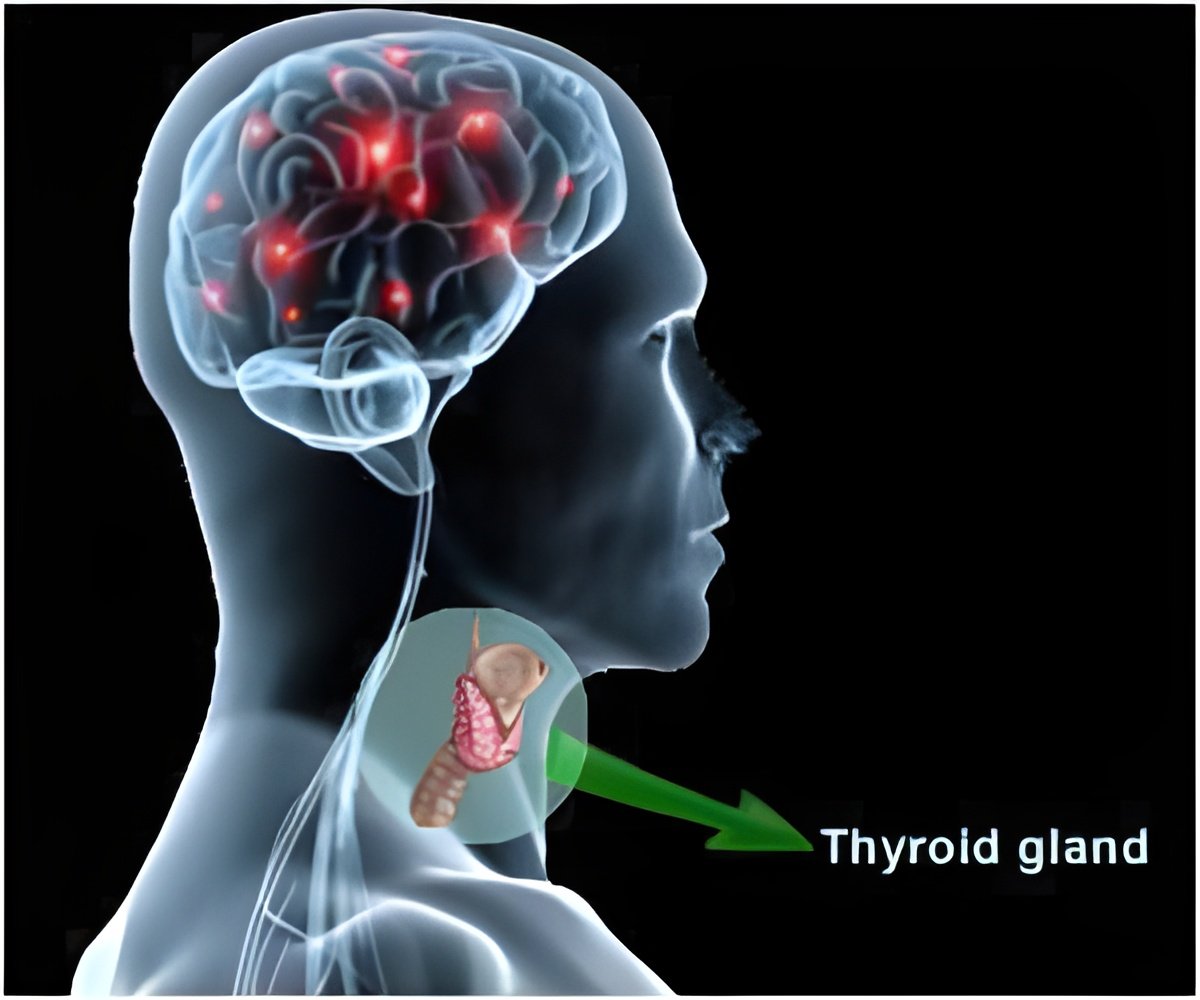
Thyroid function test is perhaps one of the most common laboratory tests performed owing to the multitude of disorders credited to thyroid dysfunction. Recent findings in individual genetic variations have led to a better understanding of the effects that thyroid hormones have on mental health. It has been found that brain–thyroid relationships are less apparent in the adult brain, though important. These are more significant in a developing brain.
To sum up, it would be wise to state that a healthy thyroid is necessary for a healthy mind. Hypothyroidism in pregnancy should be diagnosed and treated at the earliest through routine antenatal checkups. Clinically suspicious cases should be screened with a thyroid function test. National programmes exist to make sure that prevalence of iodine deficiency is kept at a low level. Areas endemic for deficiency are assigned special importance. Healthy iodine levels are important to ensure normal functionality of the thyroid.
Reference
Thyroid Disease and Mental Disorders: Cause and Effect or Only comorbidity?
Robertas Bunevièius; Arthur J. Prange Jr- Current Opinion Psychiatry. 2010;23(4):363-368.
Source-Medindia