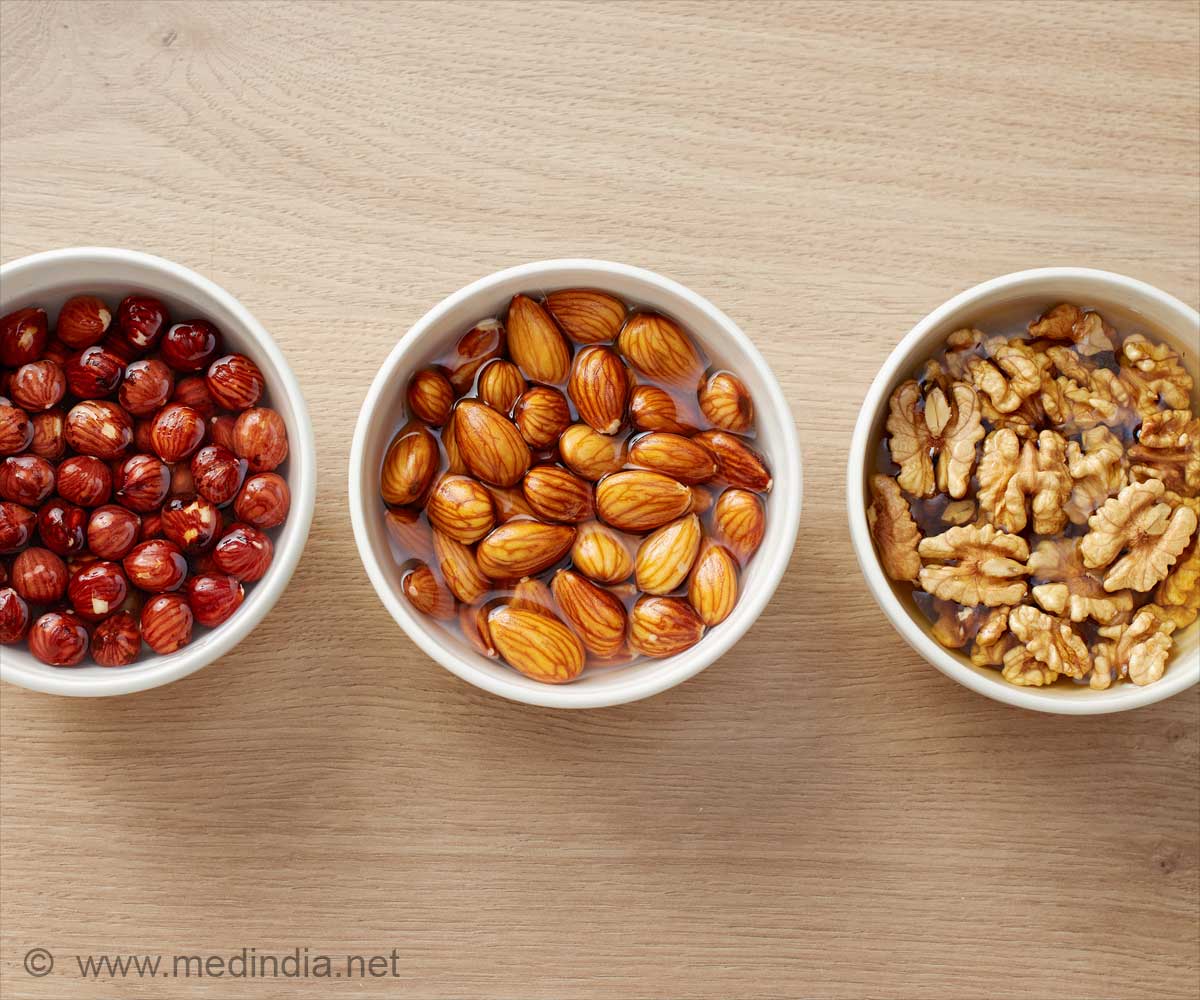
Should you soak dry fruits before eating them? Soaking almonds and raisins boosts nutrition and digestion, but cashews and pistachios are best enjoyed dry.

- Soaking almonds reduces phytic acid, making nutrients like vitamin E and magnesium more bioavailable
- Raisins become easier to digest and help regulate blood sugar when soaked before eating
- Cashews and pistachios do not require soaking as they are naturally low in phytic acid and best enjoyed dry
Soaked almonds have 10x more digestible nutrients than raw ones, but cashews and pistachios are perfectly nutritious without soaking! #healthyeating #medindia’
Almonds
Almonds are among the most popular dry fruits, thanks to their high levels of healthful fats, protein, and necessary vitamins. Soaking almonds overnight is highly suggested since it stimulates digestive enzymes and boosts nutrient availability, such as vitamin E and magnesium. Soaking almonds in water reduces their phytic acid level, a molecule that hinders the absorption of certain minerals, making the nutrients more accessible (1✔ ✔Trusted SourceDetermination of d-myo-inositol phosphates in 'activated' raw almonds using anion-exchange chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry
Go to source). Soaked almonds are also easier to chew and kinder on the stomach, making them an excellent alternative for people with digestive issues.
Raisins
Raisins are dried grapes that have a lot of energy and natural sweetness. Soaking raisins in water before eating them can provide numerous benefits, notably for digestive health. The soaking process rehydrates the raisins, making them more digestible and preventing constipation. Soaked raisins have a lower glycemic index than dried ones, which can help manage blood sugar levels.Walnuts
Walnuts include omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and vital vitamins. Walnuts also contain tannin which makes them slightly bitter and difficult to digest. Soaking them in water helps to lessen the tannin level. It also helps to neutralize phytic acid, which improves the absorption of minerals including zinc, iron, and calcium.Cashews
Unlike almonds and walnuts, cashews do not require soaking before eating. Cashews are rather soft and easy to stomach, even when raw. They have less phytic acid than other nuts, therefore soaking them has no substantial impact on their nutritional value. Furthermore, cashews have a creamy feel that is best retained when consumed dry.Pistachios
Pistachios, another dry fruit, do not benefit from soaking. These nuts are naturally low in phytic acid, thus their nutrients are readily available without soaking. Pistachios are high in protein, fiber, and healthy fats, and their crunchy texture contributes significantly to their popularity (2✔ ✔Trusted SourcePistachios for Health: What Do We Know About This Multifaceted Nut?
Go to source). Soaking pistachios may soften them and alter their flavor, so they are best enjoyed dry.
Disclaimer: The information provided here is intended for general knowledge and may not be fully research-backed. Please consult a nutritionist for personalized advice.
References:
- Determination of d-myo-inositol phosphates in 'activated' raw almonds using anion-exchange chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29808577/)
- Pistachios for Health: What Do We Know About This Multifaceted Nut? - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27340302/)
Source-Medindia