Actinic keratosis are rough, scaly patches on the skin caused by long-term exposure to sunlight and if untreated, can progress to squamous cell carcinoma.
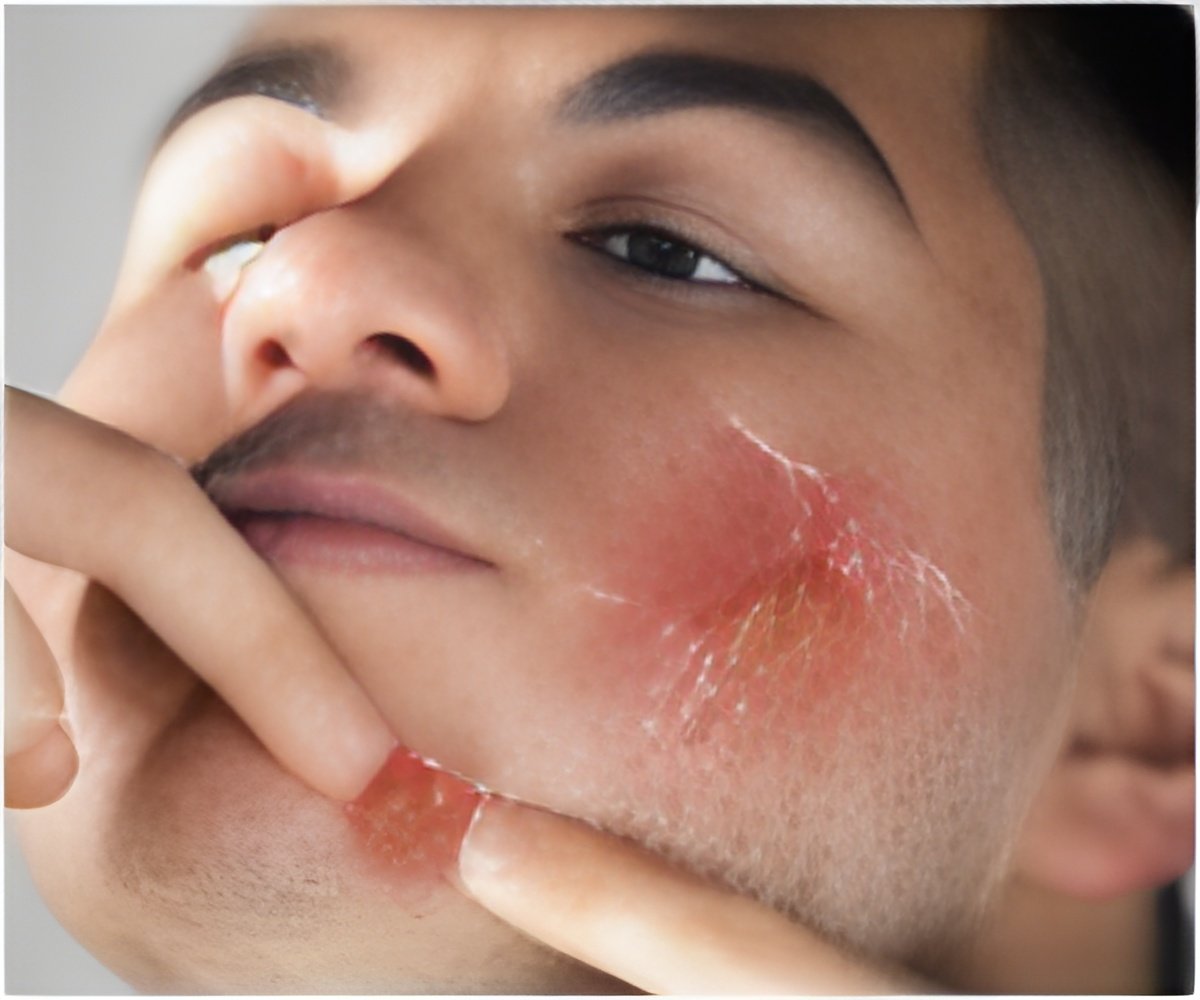

- Actinic keratosis can progress to carcinoma and is characterized by rough, scaly patches on the skin.
- Combination of a topical chemotherapy and calcipotriol helps clear actinic keratosis lesions.
- Twice-weekly application of calcipotriol both induced immune system activator and delayed tumor development. Actinic keratosis is a precursor to cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. Long treatment durations and severe side effects have limited the efficacy of current actinic keratosis treatments. The combination of a topical chemotherapy and an immune-system-activating compound was able to rapidly clear actinic keratosis lesions from patients participating in a clinical trial.
- Trevor J. Cunningham et al., Randomized trial of calcipotriol combined with 5-fluorouracil for skin cancer precursor immunotherapy, Journal of Clinical Investigation (2016), http://dx.doi.org/10.1172/JCI89820.
"The high tumor clearance rate, short treatment duration and favorable side-effect profile highlight the remarkable effectiveness of this approach, compared with currently available treatments," says Shadmehr Demehri, MD, PhD, of the MGH Center for Cancer Immunology and the Cutaneous Biology Research Center, senior author of the report.
Actinic keratosis is caused by long-term exposure to sunlight and is characterized by rough, scaly patches on the skin. The skin disease is very common in older individuals with fair complexions and if untreated, actinic keratosis lesions can progress to squamous cell carcinoma.
Current topical treatments for actinic keratosis cause side effects - such as pain, crusting and susceptibility to infection - and need to be applied for up to four weeks.
"But more importantly, the unprecedented ability of this combination therapy to directly activate the adaptive immune system against skin cancer precursors holds great promise to establish an immune memory within treated skin capable of preventing future cancer development."
Experiments with a mouse model of skin cancer development showed that twice-weekly application of calcipotriol both induced TSLP expression and delayed tumor development. When tumors did develop, they were fewer and smaller than in mice not treated with calcipotriol.
The preparations were applied twice a day to the entire affected sites of participants - face, scalp and arms - and because treatment with 5-FU alone requires seven or more days to have any effect against actinic keratosis, participants were treated for four days only. A day after treatment ended, the treated skin of those receiving calcipotriol plus 5 percent fluorouracil (5-FU) cream, including areas that did not contain clinically visible lesions, showed clear signs of inflammation, indicating immune system activation. Areas of inflammation were found to have a significant influx of lymphocytes - primarily T cells - at the sites of lesions.
Eight weeks after treatment, participants receiving the combined treatment had a significantly greater reduction in the number and size of actinic keratosis lesions - for example, an average of 88 percent reduction in facial lesions versus 26 percent reduction for those receiving the control preparation. Among participants receiving combined treatment who had previously been treated for actinic keratosis, 82 percent found the treatment to be more effective.
"As both medications used in our trial are already available clinically, they could readily be used by dermatologists to treat actinic keratosis, particular in patients for whom conventional treatments have failed," says Demehri, who is an assistant professor of Dermatology at Harvard Medical School.
"The ultimate goal of our research is to use patients' own immune systems to prevent cancer, so we are very excited to determine whether our success in activating a T-cell-dominant immune response against a skin cancer precursor will protect the treated skin against future skin cancer development. We're planning to follow the participants in this trial over the coming years to address that important question."
Reference
Source-Medindia